Comparison of Operating Conditions, Postoperative Pain and Recovery, and Overall Satisfaction of Surgeons with Deep vs. No Neuromuscular Blockade for Spinal Surgery under General Anesthesia: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 31013693
- PMCID: PMC6518127
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8040498
Comparison of Operating Conditions, Postoperative Pain and Recovery, and Overall Satisfaction of Surgeons with Deep vs. No Neuromuscular Blockade for Spinal Surgery under General Anesthesia: A Prospective Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
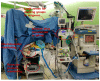
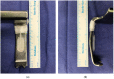
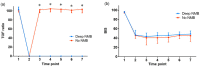
We aimed to investigate operating conditions, postoperative pain, and overall satisfaction of surgeons using deep neuromuscular blockade (NMB) vs. no NMB in patients undergoing lumbar spinal surgery under general anesthesia. Eighty-three patients undergoing lumbar fusion were randomly assigned to receive deep NMB (n = 43) or no NMB (n = 40). In the deep-NMB group, rocuronium was administered to maintain deep NMB (train-of-four count 0, post-tetanic count 1-2) until the end of surgery. In the no-NMB group, sugammadex 4 mg/kg at train-of-four (TOF) count 0-1 or sugammadex 2 mg/kg at TOF count ≥2 was administered to reverse the NMB 10 min after placing the patient prone. Peak inspiratory airway pressure, plateau airway pressure, lumbar retractor pressure significantly were lower in the deep-NMB group. Degree of surgical field bleeding (0-5), muscle tone (1-3), and satisfaction (1-10) rated by the surgeon were all superior in the deep-NMB group. Pain scores, rescue fentanyl consumption in post-anesthesia care unit (PACU), and postoperative patient-controlled analgesia consumption were significantly lower in the deep-NMB group, and this group had a shorter length of stay in PACU. Compared to no NMB, deep NMB provides better operating conditions, reduced postoperative pain and higher overall satisfaction in lumbar spinal surgery.
Keywords: neuromuscular blockade; neuromuscular monitoring; neurosurgical procedures.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of deep or moderate neuromuscular blockade for thoracoscopic lobectomy: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2018 Dec 21;18(1):195. doi: 10.1186/s12871-018-0666-6. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018. PMID: 30577757 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Recovery from prolonged deep rocuronium-induced neuromuscular blockade: A randomized comparison of sugammadex reversal with spontaneous recovery.Anaesthesist. 2015 Jul;64(7):506-12. doi: 10.1007/s00101-015-0048-0. Epub 2015 Jul 1. Anaesthesist. 2015. PMID: 26126940 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of Deep and Moderate Neuromuscular Blockade for Major Laparoscopic Surgery in Children: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Paediatr Drugs. 2024 May;26(3):347-353. doi: 10.1007/s40272-024-00622-0. Epub 2024 Mar 21. Paediatr Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38512578 Clinical Trial.
-
Deep neuromuscular block to optimize surgical space conditions during laparoscopic surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Br J Anaesth. 2017 Jun 1;118(6):834-842. doi: 10.1093/bja/aex116. Br J Anaesth. 2017. PMID: 28575335
-
Efficacy and safety of sugammadex compared to neostigmine for reversal of neuromuscular blockade: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Clin Anesth. 2016 Dec;35:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinane.2016.06.018. Epub 2016 Aug 4. J Clin Anesth. 2016. PMID: 27871504 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of rocuronium dosage on intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring in patients undergoing spinal surgery.J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022 Mar;47(3):313-320. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13557. Epub 2021 Nov 8. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2022. PMID: 34750839 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison between the trapezius and adductor pollicis muscles as an acceleromyography monitoring site for moderate neuromuscular blockade during lumbar surgery.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 15;11(1):14568. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-94062-2. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34267301 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Deep Neuromuscular Block during Robot-Assisted Transaxillary Thyroidectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial.J Clin Med. 2023 May 23;12(11):3633. doi: 10.3390/jcm12113633. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37297828 Free PMC article.
-
Cervical Disc Arthroplasty: Rationale, Designs, and Results of Randomized Controlled Trials.Int J Spine Surg. 2024 Feb 27;18(3):258-76. doi: 10.14444/8586. Online ahead of print. Int J Spine Surg. 2024. PMID: 38413235 Free PMC article.
-
Postoperative pain treatment after spinal fusion surgery: a systematic review with meta-analyses and trial sequential analyses.Pain Rep. 2022 Apr 27;7(3):e1005. doi: 10.1097/PR9.0000000000001005. eCollection 2022 May-Jun. Pain Rep. 2022. PMID: 35505790 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Groudine S.B., Soto R., Lien C., Drover D., Roberts K. A randomized, dose-finding, phase II study of the selective relaxant binding drug, Sugammadex, capable of safely reversing profound rocuronium-induced neuromuscular block. Anesth. Analg. 2007;104:555–562. doi: 10.1213/01.ane.0000260135.46070.c3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Madsen M.V., Istre O., Staehr-Rye A.K., Springborg H.H., Rosenberg J., Lund J., Gatke M.R. Postoperative shoulder pain after laparoscopic hysterectomy with deep neuromuscular blockade and low-pressure pneumoperitoneum: A randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 2016;33:341–347. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000000360. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

