Structural Insights into CB1 Receptor Biased Signaling
- PMID: 31013934
- PMCID: PMC6515405
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20081837
Structural Insights into CB1 Receptor Biased Signaling
Abstract
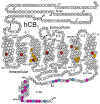
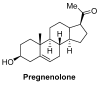
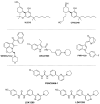
The endocannabinoid system has emerged as a promising target for the treatment of numerous diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic syndromes. Thus far, two cannabinoid receptors, CB1 and CB2, have been discovered, which are found predominantly in the central nervous system (CB1) or the immune system (CB2), among other organs and tissues. CB1 receptor ligands have been shown to induce a complex pattern of intracellular effects. The binding of a ligand induces distinct conformational changes in the receptor, which will eventually translate into distinct intracellular signaling pathways through coupling to specific intracellular effector proteins. These proteins can mediate receptor desensitization, trafficking, or signaling. Ligand specificity and selectivity, complex cellular components, and the concomitant expression of other proteins (which either regulate the CB1 receptor or are regulated by the CB1 receptor) will affect the therapeutic outcome of its targeting. With an increased interest in G protein-coupled receptors (GPCR) research, in-depth studies using mutations, biological assays, and spectroscopic techniques (such as NMR, EPR, MS, FRET, and X-ray crystallography), as well as computational modelling, have begun to reveal a set of concerted structural features in Class A GPCRs which relate to signaling pathways and the mechanisms of ligand-induced activation, deactivation, or activity modulation. This review will focus on the structural features of the CB1 receptor, mutations known to bias its signaling, and reported studies of CB1 receptor ligands to control its specific signaling.
Keywords: CB1 receptor; biased signaling; cannabinoids; functional selectivity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


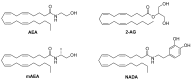
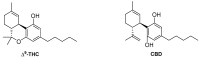
Similar articles
-
Cannabinoid receptor 1 ligands: Biased signaling mechanisms driving functionally selective drug discovery.Pharmacol Ther. 2025 Mar;267:108795. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2025.108795. Epub 2025 Jan 17. Pharmacol Ther. 2025. PMID: 39828030 Review.
-
The cannabinoid receptor CB1 modulates the signaling properties of the lysophosphatidylinositol receptor GPR55.J Biol Chem. 2012 Dec 28;287(53):44234-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.364109. Epub 2012 Nov 16. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23161546 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological data of cannabidiol- and cannabigerol-type phytocannabinoids acting on cannabinoid CB1, CB2 and CB1/CB2 heteromer receptors.Pharmacol Res. 2020 Sep;159:104940. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2020.104940. Epub 2020 May 26. Pharmacol Res. 2020. PMID: 32470563
-
Structure of a Signaling Cannabinoid Receptor 1-G Protein Complex.Cell. 2019 Jan 24;176(3):448-458.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.11.040. Epub 2019 Jan 10. Cell. 2019. PMID: 30639101 Free PMC article.
-
CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling and Biased Signaling.Molecules. 2021 Sep 6;26(17):5413. doi: 10.3390/molecules26175413. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34500853 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Medical Cannabis in Treatment of Resistant Familial Mediterranean Fever.Am J Case Rep. 2019 Sep 10;20:1340-1342. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.917180. Am J Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 31501406 Free PMC article.
-
All-Atom Molecular Dynamics Simulations Indicated the Involvement of a Conserved Polar Signaling Channel in the Activation Mechanism of the Type I Cannabinoid Receptor.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 20;24(4):4232. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044232. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835641 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the therapeutic potential of natural compounds modulating the endocannabinoid system in various diseases and disorders: review.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Dec;75(6):1410-1444. doi: 10.1007/s43440-023-00544-7. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37906390 Review.
-
Structural basis of THC analog activity at the Cannabinoid 1 receptor.Nat Commun. 2025 Jan 8;16(1):486. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-55808-4. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 39779700 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Structure, Function, and Pharmacology of Class A Lipid GPCRs: Opportunities and Challenges for Drug Discovery.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Dec 22;15(1):12. doi: 10.3390/ph15010012. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35056070 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Devane W.A., Dysarz F.A., Johnson M.R., Melvin L.S., Howlett A.C. Determination and characterization of a cannabinoid receptor in rat brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 1988;34:605–613. - PubMed
-
- Fernández-Ruiz J., Romero J., Ramos J.A. Endocannabinoids and Neurodegenerative Disorders: Parkinson’s Disease, Huntington’s Chorea, Alzheimer’s Disease, and Others. In: Pertwee R.G., editor. Endocannabinoids. Volume 231. Springer International Publishing; Cham, Switzerland: 2015. pp. 233–259. Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

