CFM-ID 3.0: Significantly Improved ESI-MS/MS Prediction and Compound Identification
- PMID: 31013937
- PMCID: PMC6523630
- DOI: 10.3390/metabo9040072
CFM-ID 3.0: Significantly Improved ESI-MS/MS Prediction and Compound Identification
Abstract
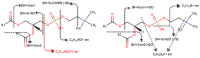
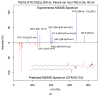
Metabolite identification for untargeted metabolomics is often hampered by the lack of experimentally collected reference spectra from tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS). To circumvent this problem, Competitive Fragmentation Modeling-ID (CFM-ID) was developed to accurately predict electrospray ionization-MS/MS (ESI-MS/MS) spectra from chemical structures and to aid in compound identification via MS/MS spectral matching. While earlier versions of CFM-ID performed very well, CFM-ID's performance for predicting the MS/MS spectra of certain classes of compounds, including many lipids, was quite poor. Furthermore, CFM-ID's compound identification capabilities were limited because it did not use experimentally available MS/MS spectra nor did it exploit metadata in its spectral matching algorithm. Here, we describe significant improvements to CFM-ID's performance and speed. These include (1) the implementation of a rule-based fragmentation approach for lipid MS/MS spectral prediction, which greatly improves the speed and accuracy of CFM-ID; (2) the inclusion of experimental MS/MS spectra and other metadata to enhance CFM-ID's compound identification abilities; (3) the development of new scoring functions that improves CFM-ID's accuracy by 21.1%; and (4) the implementation of a chemical classification algorithm that correctly classifies unknown chemicals (based on their MS/MS spectra) in >80% of the cases. This improved version called CFM-ID 3.0 is freely available as a web server. Its source code is also accessible online.
Keywords: MS spectral prediction; combinatorial fragmentation; liquid chromatography; mass spectrometry; metabolite identification; rule-based fragmentation; structure-based chemical classification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Lynn K.S., Cheng M.L., Chen Y.R., Hsu C., Chen A., Lih T.M., Chang H.Y., Huang C.J., Shiao M.S., Pan W.H., et al. Metabolite identification for mass spectrometry-based metabolomics using multiple types of correlated ion information. Anal. Chem. 2015;87:2143–2151. doi: 10.1021/ac503325c. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sumner L.W., Amberg A., Barrett D., Beale M.H., Beger R., Daykin C.A., Fan T.W., Fiehn O., Goodacre R., Griffin J.L., et al. Proposed minimum reporting standards for chemical analysis Chemical Analysis Working Group (CAWG) Metabolomics Standards Initiative (MSI) Metabolomics. 2007;3:211. doi: 10.1007/s11306-007-0082-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Schymanski E.L., Singer H.P., Longrée P., Loos M., Ruff M., Stravs M.A., Ripollés Vidal C., Hollender J. Strategies to characterize polar organic contamination in wastewater: Exploring the capability of high resolution mass spectrometry. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014;48:1811–1818. doi: 10.1021/es4044374. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

