Return to Work Interventions for Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and a Methodological Critique
- PMID: 31014004
- PMCID: PMC6518012
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16081343
Return to Work Interventions for Cancer Survivors: A Systematic Review and a Methodological Critique
Abstract
Cancer patients are more at risk of being unemployed or having difficulties to return to work (RTW) compared to individuals without health concerns, and is thus a major public health issue. The aim of this systematic review is to identify and describe the interventions developed specifically to help cancer patients to RTW after treatment. Two researchers independently screened the articles for inclusion and Critical Appraisal Skills Program (CASP) checklists were used to assess the methodology of the included studies. Ten manuscripts met the inclusion criteria. The type of studies were three quasi-experimental studies, three longitudinal studies, three randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and a qualitative study. RTW interventions were conducted in or outside the hospital (n = 6 and 3 respectively), or both (n = 1). Improvements in RTW were only observed in quasi-experimental studies. No improvement in RTW was noted in RCTs, nor in other measures (e.g., quality of life, fatigue). Lack of statistically significant improvement does not necessarily reflect reality, but may be attributed to non-adapted research methods. This systematic review underscores the need for researches in the RTW field to reach a consensus on RTW criteria and their assessment. Recommendations to this effect are suggested.
Keywords: cancer; intervention; return to work; systematic review; work rehabilitation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
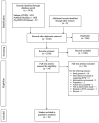
Figures
References
-
- The Global Cancer Observatory World Fact Sheets. [(accessed on 28 December 2018)];2018 Available online: http://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/900-world-fact-shee....
-
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare Cancer in Australia 2017. [(accessed on 10 September 2018)]; Available online: https://www.aihw.gov.au/getmedia/3da1f3c2-30f0-4475-8aed-1f19f8e16d48/20....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous