Selenocompounds as Novel Antibacterial Agents and Bacterial Efflux Pump Inhibitors
- PMID: 31014009
- PMCID: PMC6514980
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24081487
Selenocompounds as Novel Antibacterial Agents and Bacterial Efflux Pump Inhibitors
Abstract
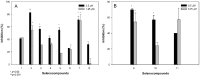
Bacterial multidrug resistance is becoming a growing problem for public health, due to the development and spreading of bacterial strains resistant to antimicrobials. In this study, the antibacterial and multidrug resistance reversing activity of a series of seleno-carbonyl compounds has been evaluated. The effects of eleven selenocompounds on bacterial growth were evaluated in Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA), Enterococcus faecalis, Escherichia coli, and Chlamydia trachomatis D. The combination effect of compounds with antibiotics was examined by the minimum inhibitory concentration reduction assay. Their efflux pump (EP) inhibitory properties were assessed using real-time fluorimetry. Relative expressions of EP and quorum-sensing genes were studied by quantitative PCR. Results showed that a methylketone selenoester had remarkable antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria and potentiated the activity of oxacillin in MRSA. Most of the selenocompounds showed significant anti-chlamydial effects. The selenoanhydride and the diselenodiester were active inhibitors of the AcrAB-TolC system. Based on these results it can be concluded that this group of selenocompounds can be attractive potential antibacterials and EP inhibitors. The discovery of new derivatives with a significant antibacterial activity as novel selenocompounds, is of high impact in the fight against resistant pathogens.
Keywords: AcrAB-TolC efflux pump; Chlamydia trachomatis D; Escherichia coli K-12 AG100; Staphylococcus aureus; selenocompounds; selenoesters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
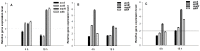
References
-
- Angeli A., Abbas G., del Prete S., Capasso C., Supuran C.T. Selenides bearing benzenesulfonamide show potent inhibition activity against carbonic anhydrases from pathogenic bacteria Vibrio cholerae and Burkholderia pseudomallei. Bioorg. Chem. 2018;79:319–322. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.05.015. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

