The incidence of acute kidney injury following cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation in a rat model
- PMID: 31014141
- PMCID: PMC6493295
- DOI: 10.1080/0886022X.2019.1596819
The incidence of acute kidney injury following cardiac arrest and cardiopulmonary resuscitation in a rat model
Abstract
Objective: In the current study, we investigated the incidence of acute kidney injury (AKI) induced by cardiac arrest (CA) and cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and whether such an AKI can recover spontaneously in rats.
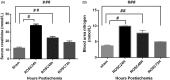
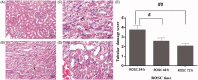
Methods: We used transesophageal alternating current stimulation to establish 7 min of CA rat model followed by conventional CPR. The experimental rats were randomly divided into three groups (n = 20 per group) according to the different time points after restoration spontaneous circulation (ROSC): the ROSC 24 h, ROSC 48 h, and ROSC 72 h group. The diagnosis of rat AKI refers to the 2012 KDIGO adult AKI diagnostic criteria. The severity of AKI quantified by the serum creatinine (SCR), blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels and histological features of renal tissue.
Results: The incidence rates of AKI in ROSC 24 h, ROSC 48 h, and ROSC 72 h group were 65%, 45%, and 42.9%. Moreover, the values of SCR and BUN were highest at ROSC 24 h, and then gradually decreased with the time of ROSC. The histological changes of the renal tissues such as glomerular collapse, renal tubular cell swelling, and inflammatory cell infiltration had also observed.
Conclusion: The incidence of AKI in rats was high after suffering from CA and CPR, but renal function improved with the prolongation of ROSC time, indicating the ability of the kidney to self-repair.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; cardiac arrest; cardiopulmonary resuscitation; ischemia-reperfusion injury; rat.
Figures
References
-
- Webb S, Dobb G. ARF, ATN or AKI? It's now acute kidney injury. Anaesth Intensive Care. 2007;35:843. - PubMed
-
- Uchino S, Kellum JA, Bellomo R, et al. Acute renal failure in critically ill patients: a multinational, multicenter study. JAMA. 2005;294:813–818. - PubMed
-
- Mattana J, Singhal PC. Prevalence and determinants of acute renal failure following cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Arch Intern Med. 1993;153:235–239. - PubMed
-
- Geri G, Guillemet L, Dumas F, et al. Acute kidney injury after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest: risk factors and prognosis in a large cohort. Intensive Care Med. 2015;41:1273–1280. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
