Advance care planning dispositions: the relationship between knowledge and perception
- PMID: 31014271
- PMCID: PMC6480869
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-019-1113-3
Advance care planning dispositions: the relationship between knowledge and perception
Abstract
Background: Legal dispositions for advance care planning (ACP) are available but used by a minority of older adults in Switzerland. Some studies found that knowledge of and perception of those dispositions are positively associated with their higher usage. The objective of the present study is to test the hypothesis of an association between increased knowledge of ACP dispositions and a more positive perception of them.
Methods: Data collected in 2014 among 2125 Swiss community-dwellers aged 71 to 80 of the Lausanne cohort 65+ (Lc65+), a population-based longitudinal study on aging and frailty. Data collection was conducted through a questionnaire on knowledge, use and perception of lasting power of attorney, advance directives and designation of a health care proxy. Covariables were extracted from the Lc65+ database. Bivariable and multivariable regression analyses assessed the association between level of knowledge and perception.
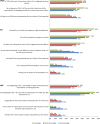
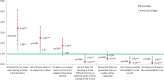
Results: Half the participants did not know about legal dispositions for ACP; filing rates were 14% for advance directives, 11% for health care proxy and 6% for lasting power of attorney. Level of knowledge about the dispositions was associated with a more positive perception of them, even when adjusting for confounding factors.
Conclusion: Although the direction of the association's causality needs more investigation, results indicate that better knowledge on ACP dispositions could improve the perception older people have of them. Communication on dispositions should take into account individual knowledge levels and address commonly enunciated barriers that seem to diminish with increased knowledge.
Keywords: Advance care planning; Advance directives; Health care proxy; Knowledge; Perception.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
According to Swiss Federal Law 118b on human subject research (C.f.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Harringer W, Hoby G. Dispositions de fin de vie des patients dans le cadre pratique du médecin de famille. Prim Res. 2009;9(3):56–58.
-
- Schwarzenegger C, Manzoni P, Studer D, Leanza C. Was die Schweizer Bevölkerung von Sterbehilfe und Suizidbeihilfe hält? Jusletter 13. 2010.
-
- Pautex Sophie, Gamondi Claudia, Philippin Yves, Gremaud Grégoire, Herrmann François, Camartin Cristian, Vayne-Bossert Petra. Advance directives and end-of-life decisions in Switzerland: role of patients, relatives and health professionals. BMJ Supportive & Palliative Care. 2015;8(4):475–484. doi: 10.1136/bmjspcare-2014-000730. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Merçay C. Expérience de la population âgée de 65 ans et plus avec le système de santé. Neuchâtel, Switzerland: Swiss Health. Observatory. 2017; Report No.: 60.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

