LASIK-induced corneal changes after correction of hyperopia with and without application of Mitomycin-C
- PMID: 31014283
- PMCID: PMC6480872
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-019-1100-7
LASIK-induced corneal changes after correction of hyperopia with and without application of Mitomycin-C
Abstract
Background: The study aimed to assess the role of intraoperative mitomycin-C (MMC) application during hyperopic LASIK correction (+ 1.00 D to + 6.00 D) by examining topographic corneal changes and incidence of regression over a one-year follow-up period.
Methods: This comparative randomized control study included 68 hyperopic patients (136 eyes) divided into two groups; Group A included 34 patients (68 eyes) that had LASIK with the application of 0.02% MMC for 10 s on the stromal bed after excimer laser treatment, and group B included 34 patients (68 eyes) that had LASIK without MMC application. Uncorrected distance visual acuity (UDVA), refraction, keratometry and topography were recorded at 1st week and 1st, 3rd, 6th, and 12th months postoperation. Predictability and treatment efficacy were also recorded at the end of the follow-up period.
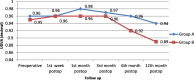
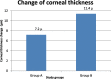
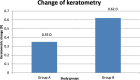
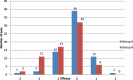
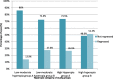
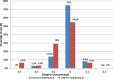
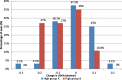
Results: Better predictability was noted in group A than in group B at the 6 month and 12 month follow-up visits, with a mean cycloplegic refraction SE of + 0.5 ± 0.31 D in group A and + 0.67 ± 0.39 D in group B at the 6 month visit, and + 0.63 ± 0.37 D in group A and + 0.89 ± 0.48 D in group B at the 12 month visit. The efficacy of the treatment at the end of the follow up period was better in group A than in group B. Group A showed fewer topographic corneal changes than group B.
Conclusions: Intraoperative MMC application during hyperopic LASIK achieves better predictability and efficacy and induces fewer topographic changes and lower regression rate of hyperopia during the first postoperative year.
Trial registration: the Pan African Clinical Trial Registry PACTR201901543722087 , on 29 January 2019.
Keywords: Hyperopic LASIK - regression; Mitomycin-C.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Informed written consent was obtained from all study individuals. This study was approved by the Departmental Research Committee and Research Ethics Committee, Faculty of medicine, Suez Canal University on (14/2/2016) with a reference number (research #2717) and followed the tenets of Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication
Consent for the publication of identifying images or other personal or clinical details of participants that compromise anonymity is not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Anschutz T. Laser correction of hyperopia and presbyopia. Int Ophthalmol Clin. 1994;42:139–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

