Molluscicidal effectiveness of Luo-Wei, a novel plant-derived molluscicide, against Oncomelania hupensis, Biomphalaria alexandrina and Bulinus truncatus
- PMID: 31014390
- PMCID: PMC6480903
- DOI: 10.1186/s40249-019-0535-7
Molluscicidal effectiveness of Luo-Wei, a novel plant-derived molluscicide, against Oncomelania hupensis, Biomphalaria alexandrina and Bulinus truncatus
Erratum in
-
Corrections to: Molluscicidal effectiveness of Luo-Wei, a novel plant-derived molluscicide, against Oncomelania hupensis, Biomphalaria alexandrina and Bulinus truncatus.Infect Dis Poverty. 2019 Jun 6;8(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s40249-019-0548-2. Infect Dis Poverty. 2019. PMID: 31171036 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Control of snail intermediate hosts has been proved to be a fast and efficient approach for interrupting the transmission of schistosomiasis. Some plant extracts have shown obvious molluscicidal activity, and a new compound Luo-Wei, also named tea-seed distilled saponin (TDS), was developed based on the saponins extracted from Camellia oleifera seeds. We aimed to test the molluscicidal activity of 4% TDS against the intermediate host snails in China and Egypt, and evaluate its environmental safety to non-target organisms.
Methods: In the laboratory, Oncomelania hupensis, Biomphalaria alexandrina and Bulinus truncatus were exposed to 4% TDS, and the median lethal concentration (LC50) was estimated at 24, 48 and 72 h. In the field, snail mortalities were assessed 1, 2, 3 and 7 d post-immersion with 2.5 g/m3 4% TDS and 1, 3, 7 and 15 d post-spraying with 5 g/m2 4% TDS. In addition, the acute toxicity of 4% TDS to Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica), zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio) and freshwater shrimp (Macrobrachium nipponense) was assessed by estimations of LC50 or median lethal dose (LD50).
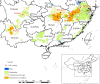
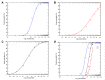
Results: In the laboratory, the LC50 values of 4% TDS for O. hupensis were 0.701, 0.371 and 0.33 mg/L at 24, 48 and 72 h, respectively, and 4% TDS showed a 1.975 mg/L [corrected] 24 h LC50 against B. alexandrina, and a 1.396 mg/L 24 h LC50 against B. truncatus. Across all study regions, the pooled mortalities of O. hupensis were 72, 86, 94 and 98% at 1, 2, 3 and 7 d, following field immersion of 4% TDS at a dose of 2.5 g/m3, and were 69, 77, 85 and 88% at 1, 3, 7 and 15 d, following field spraying at 5 g/m2, respectively. 4% TDS had moderate toxicity to Japanese quail (7 d LD50 > 60 mg/kg) and to shrimp (96 h LC50 = 6.28 mg/L; 95% CI: 3.53-11.2 mg/L), whereas its toxicity to zebrafish was high (96 h LC50 = 0.15 mg/L; 95% CI: 0.14-0.17 mg/L).
Conclusions: 4% TDS is active against O. hupensis, B. alexandrina and B. truncatus under laboratory and field conditions, and it may be a candidate molluscicide of plant origin.
Keywords: Biomphalaria alexandrina; Bulinus truncatus; Luo-Wei; Molluscicidal activity; Oncomelania hupensis; Plant-derived molluscicide; Schistosomiasis.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors consent for publication of this manuscript.
Competing interests
Prof. Xiao-Nong Zhou is the Editor-in-Chief of
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Field evaluation of a novel plant molluscicide "Luo-wei" against the snail Oncomelania hupensis III molluscicidal effect by spraying method in hilly regions].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2013 Oct;25(5):495-7. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24490361 Chinese.
-
[Molluscicidal activity of 25% wettable powder of pyriclobenzuron sulphate against Oncomelania hupensis robertsoni].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2019 Apr 30;31(2):115-120. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2019014. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31184039 Chinese.
-
[Field evaluation of a novel plant molluscicide "Luo-Wei" against Oncomelania hupensis I molluscicidal effect by the spraying method in lake and marshland regions].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2013 Apr;25(2):125-8. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 23894829 Chinese.
-
Exploring the immune interactions between Oncomelania hupensis and Schistosoma japonicum, with a cross-comparison of immunological research progress in other intermediate host snails.Parasit Vectors. 2023 Dec 13;16(1):453. doi: 10.1186/s13071-023-06011-9. Parasit Vectors. 2023. PMID: 38093363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Application of drones in Oncomelania hupensis snail control with molluscicides].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2024 Nov 11;36(5):439-440. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1915.2024188. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 39623983 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Molluscicidal and parasiticidal activities of Eryngium triquetrum essential oil on Schistosoma mansoni and its intermediate snail host Biomphalaria glabrata, a double impact.Parasit Vectors. 2020 Sep 23;13(1):486. doi: 10.1186/s13071-020-04367-w. Parasit Vectors. 2020. PMID: 32967724 Free PMC article.
-
The identification of alternative oxidase in intermediate host snails of Schistosoma and its potential role in protecting Oncomelania hupensis against niclosamide-induced stress.Parasit Vectors. 2022 Mar 21;15(1):97. doi: 10.1186/s13071-022-05227-5. Parasit Vectors. 2022. PMID: 35313980 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the molluscicidal activities of arylpyrrole on Oncomelania hupensis, the intermediate host of Schistosoma japonicum.PeerJ. 2021 Sep 27;9:e12209. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12209. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34692251 Free PMC article.
-
Biocontrol potential of Arabidopsis thaliana against Biomphalaria glabrata, the intermediate host of Schistosoma mansoni, focusing on biological, physiological, histopathological, and genotoxic impacts.Parasite Epidemiol Control. 2025 May 12;30:e00428. doi: 10.1016/j.parepi.2025.e00428. eCollection 2025 Aug. Parasite Epidemiol Control. 2025. PMID: 40502385 Free PMC article.
-
Corrections to: Molluscicidal effectiveness of Luo-Wei, a novel plant-derived molluscicide, against Oncomelania hupensis, Biomphalaria alexandrina and Bulinus truncatus.Infect Dis Poverty. 2019 Jun 6;8(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s40249-019-0548-2. Infect Dis Poverty. 2019. PMID: 31171036 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sola P, Mvumi BM, Ogendo JO, Mponda O, Kamanula JF, Nyirenda SP, Belmain SR, Stevenson PC. Botanical pesticide production, trade and regulatory mechanisms in sub-Saharan Africa: making a case for plant-based pesticidal products. Food Secur. 2014;6:369–384. doi: 10.1007/s12571-014-0343-7. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2009BAI78B07/National Science and Technology Pillar Program/International
- 2009BAI78B04/National Science and Technology Pillar Program/International
- 2012ZX10004-220/National S & T Major Program/International
- 11XD1405400/Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (CN)/International
- QNRC2016621/Jiangsu Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

