Deprivation and threat, emotion dysregulation, and psychopathology: Concurrent and longitudinal associations
- PMID: 31014408
- PMCID: PMC7012774
- DOI: 10.1017/S0954579419000294
Deprivation and threat, emotion dysregulation, and psychopathology: Concurrent and longitudinal associations
Abstract
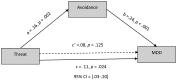
Maltreatment increases risk for psychopathology in childhood and adulthood, thus identifying mechanisms that influence these associations is necessary for future prevention and intervention. Emotion dysregulation resulting from maltreatment is one potentially powerful mechanism explaining risk for psychopathology. This study tests a conceptual model that distinguishes deprivation and threat as distinct forms of exposure with different pathways to psychopathology. Here we operationalize threat as exposure to physical and/or sexual abuse and deprivation as exposure to neglect. We test the hypothesis that threat and deprivation differentially predict use of avoidant strategies and total regulation. Data were drawn from the Longitudinal Studies on Child Abuse and Neglect (LONGSCAN study; N = 866), which followed high-risk children from age 4 to 18. At age 6, children and their parents reported on adversity exposure. Case records documented exposure to abuse and neglect. At 18, adolescents reported on regulation strategies and psychopathology. Regression analyses indicated that greater exposure to threat, but not deprivation, predicted greater use of avoidant strategies in adolescence. Moreover, avoidance partially mediated the longitudinal association between exposure to threat in early childhood and symptoms of internalizing psychopathology in adolescence. Results suggest that abuse and neglect differentially predict regulation strategy use and that regulation strategy use predicts psychopathology.
Keywords: Dimensional Model of Adversity and Psychopathology; abuse; emotion dysregulation; maltreatment; neglect; psychopathology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Difficulties with emotion regulation as a transdiagnostic mechanism linking child maltreatment with the emergence of psychopathology.Dev Psychopathol. 2019 Aug;31(3):899-915. doi: 10.1017/S0954579419000348. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Dev Psychopathol. 2019. PMID: 30957738 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Patterns of Delayed Emotion Circuit Maturation in Abused Girls With and Without Internalizing Psychopathology.Am J Psychiatry. 2021 Nov;178(11):1026-1036. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2021.20081192. Epub 2021 Aug 19. Am J Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 34407623 Free PMC article.
-
Dimensions of deprivation and threat, psychopathology, and potential mediators: A multi-year longitudinal analysis.J Abnorm Psychol. 2018 Feb;127(2):160-170. doi: 10.1037/abn0000331. J Abnorm Psychol. 2018. PMID: 29528670 Free PMC article.
-
Alexithymia in individuals maltreated as children and adolescents: a meta-analysis.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2022 Sep;63(9):963-972. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.13616. Epub 2022 Apr 19. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35438190 Review.
-
Child Maltreatment and Risk for Psychopathology in Childhood and Adulthood.Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2017 May 8;13:525-551. doi: 10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032816-045005. Epub 2017 Mar 30. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2017. PMID: 28375720 Review.
Cited by
-
Threat, Emotion Dysregulation, and Parenting in a Clinical Sample of Children with Disruptive Behaviour.Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2024 Jul 5. doi: 10.1007/s10578-024-01729-8. Online ahead of print. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev. 2024. PMID: 38967709
-
Verbal Weight-Related Abuse and Binge Eating Behavior: The Mediating Role of Attentional Bias to Threat Cues and Difficulties in Emotion Regulation.Brain Behav. 2024 Oct;14(10):e70054. doi: 10.1002/brb3.70054. Brain Behav. 2024. PMID: 39344340 Free PMC article.
-
Cognitive stimulation as a mechanism linking socioeconomic status and neural function supporting working memory: a longitudinal fMRI study.Cereb Cortex. 2024 Jan 31;34(2):bhad545. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhad545. Cereb Cortex. 2024. PMID: 38236725 Free PMC article.
-
Mediating Effects of Specific Types of Coping Styles on the Relationship between Childhood Maltreatment and Depressive Symptoms among Chinese Undergraduates: The Role of Sex.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Apr 30;17(9):3120. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17093120. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32365812 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship Between Temperament Characteristics and Emotion Regulation Abilities in Institutionalized and Noninstitutionalized Children.Psychol Stud (Mysore). 2023 May 16:1-13. doi: 10.1007/s12646-023-00735-5. Online ahead of print. Psychol Stud (Mysore). 2023. PMID: 37361514 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alink L. R., Cicchetti D., Kim J., & Rogosch F. A. (2009). Mediating and moderating processes in the relation between maltreatment and psychopathology: Mother-child relationship quality and emotion regulation. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37, 831–843. doi:10.1007/s10802-009-9314-4 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

