Dose-dependent atrophy of the amygdala after radiotherapy
- PMID: 31015128
- PMCID: PMC7041546
- DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.03.024
Dose-dependent atrophy of the amygdala after radiotherapy
Abstract
Background and purpose: The amygdalae are deep brain nuclei critical to emotional processing and the creation and storage of memory. It is not known whether the amygdalae are affected by brain radiotherapy (RT). We sought to quantify dose-dependent amygdala change one year after brain RT.
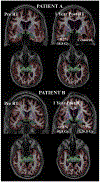
Materials and methods: 52 patients with primary brain tumors were retrospectively identified. Study patients underwent high-resolution, volumetric magnetic resonance imaging before RT and 1 year afterward. Images were processed using FDA-cleared software for automated segmentation of amygdala volume. Tumor, surgical changes, and segmentation errors were manually censored. Mean amygdala RT dose was tested for correlation with amygdala volume change 1 year after RT via the Pearson correlation coefficient. A linear mixed-effects model was constructed to evaluate potential predictors of amygdala volume change, including age, tumor hemisphere, sex, seizure history, and bevacizumab treatment during the study period. As 51 of 52 patients received chemotherapy, possible chemotherapy effects could not be studied. A two-tailed p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
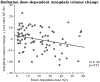
Results: Mean amygdala RT dose (r = -0.28, p = 0.01) was significantly correlated with volume loss. On multivariable analysis, the only significant predictor of amygdala atrophy was radiation dose. The final linear mixed-effects model estimated amygdala volume loss of 0.17% for every 1 Gy increase in mean amygdala RT dose (p = 0.008).
Conclusions: The amygdala demonstrates dose-dependent atrophy one year after radiotherapy for brain tumors. Amygdala atrophy may mediate neuropsychological effects seen after brain RT.
Keywords: Amygdala; Brain radiotherapy; Quantitative MRI.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiation Dose-Dependent Hippocampal Atrophy Detected With Longitudinal Volumetric Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017 Feb 1;97(2):263-269. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2016.10.035. Epub 2016 Oct 31. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017. PMID: 28068234 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebral Cortex Regions Selectively Vulnerable to Radiation Dose-Dependent Atrophy.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017 Apr 1;97(5):910-918. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.01.005. Epub 2017 Jan 6. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017. PMID: 28333012 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-Dependent Cortical Thinning After Partial Brain Irradiation in High-Grade Glioma.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016 Feb 1;94(2):297-304. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.10.026. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016. PMID: 26853338 Free PMC article.
-
Dose-Dependent Atrophy in Bilateral Amygdalae and Nuclei After Brain Radiation Therapy and Its Association With Mood and Memory Outcomes on a Longitudinal Clinical Trial.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023 Nov 15;117(4):834-845. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.05.026. Epub 2023 May 24. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2023. PMID: 37230430
-
Salvage treatment for recurrent intracranial germinoma after reduced-volume radiotherapy: a single-institution experience and review of the literature.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 Nov 1;84(3):639-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.12.052. Epub 2012 Feb 21. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. PMID: 22361082 Review.
Cited by
-
Dose-dependent volume loss in subcortical deep grey matter structures after cranial radiotherapy.Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2020 Nov 15;26:35-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ctro.2020.11.005. eCollection 2021 Jan. Clin Transl Radiat Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33294645 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the potential of diffusion tensor imaging biomarkers in prediction of white matter changes after brain radiation therapy: A systematic review.J Res Med Sci. 2025 Apr 30;30:20. doi: 10.4103/jrms.jrms_234_24. eCollection 2025. J Res Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40391343 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MR Image Changes of Normal-Appearing Brain Tissue after Radiotherapy.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 29;13(7):1573. doi: 10.3390/cancers13071573. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancing Beyond the Hippocampus to Preserve Cognition for Patients With Brain Metastases: Dosimetric Results From a Phase 2 Trial of Memory-Avoidance Whole Brain Radiation Therapy.Adv Radiat Oncol. 2023 Aug 10;9(2):101337. doi: 10.1016/j.adro.2023.101337. eCollection 2024 Feb. Adv Radiat Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38405310 Free PMC article.
-
Microstructural Injury to Corpus Callosum and Intrahemispheric White Matter Tracts Correlate With Attention and Processing Speed Decline After Brain Radiation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021 Jun 1;110(2):337-347. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.12.046. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2021. PMID: 33412257 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

