Relationship between neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and short-term prognosis in the chronic obstructive pulmonary patients with acute exacerbation
- PMID: 31015366
- PMCID: PMC6522720
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20190675
Relationship between neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio and short-term prognosis in the chronic obstructive pulmonary patients with acute exacerbation
Abstract
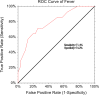
We retrospectively collected data from a large sample size of population and explore the relationship between neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and adverse outcomes, and assessed the clinical prognostic utility of NLR in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary patients with acute exacerbation (AECOPD). We reviewed 3 years medical case records, 622 patients were identified including 48 died and 574 alive. Compared with alive group, the died group had significantly elevated neutrophils, lymphocyte, and NLR level (P<0.001). The high-sensitive C-protein level of died group was also higher compared with alive group (7.48 ± 4.2 vs 1.26 ± 0.56, vs P<0.001). The univariate logistic regression indicated that elevated NLR level was associated with the increased of adverse outcome (odds ratio [OR] = 4.59, 95% CI: 2.27-8.94, P<0.001). After adjusted potential confounding factors, the elevated NLR level was still associated with adverse outcomes in the chronic obstructive pulmonary patients with acute exacerbation (OR = 2.05, 95% CI: 1.21-3.48, P=0.008). The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve for death at 90 days was 0.742 (95% CI: 0.554-0.881). NLR cutoff of >4.19 had a sensitivity of 71.4% and specificity of 74.2%. Our results suggested that NLR, as a rapid, inexpensive and easily obtained blood routine index was associated with short-term adverse outcomes in patients with AECOPD. The elevated NLR predicted the increased the risk of 90-day mortality in patients with AECOPD.
Keywords: COPD; chronic obstructive pulmonary patients; neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; prognosis.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Vogelmeier C.F., Criner G.J., Martinez F.J., Anzueto A., Barnes P.J., Bourbeau J.. et al. (2017) Global Strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease 2017 report: GOLD executive summary. Eur. Respir. J. 49, 557–582 10.1183/13993003.00214-2017 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical