The histone chaperoning pathway: from ribosome to nucleosome
- PMID: 31015382
- PMCID: PMC6484783
- DOI: 10.1042/EBC20180055
The histone chaperoning pathway: from ribosome to nucleosome
Abstract
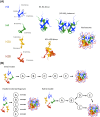
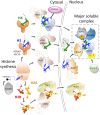
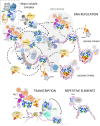
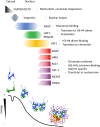
Nucleosomes represent the fundamental repeating unit of eukaryotic DNA, and comprise eight core histones around which DNA is wrapped in nearly two superhelical turns. Histones do not have the intrinsic ability to form nucleosomes; rather, they require an extensive repertoire of interacting proteins collectively known as 'histone chaperones'. At a fundamental level, it is believed that histone chaperones guide the assembly of nucleosomes through preventing non-productive charge-based aggregates between the basic histones and acidic cellular components. At a broader level, histone chaperones influence almost all aspects of chromatin biology, regulating histone supply and demand, governing histone variant deposition, maintaining functional chromatin domains and being co-factors for histone post-translational modifications, to name a few. In this essay we review recent structural insights into histone-chaperone interactions, explore evidence for the existence of a histone chaperoning 'pathway' and reconcile how such histone-chaperone interactions may function thermodynamically to assemble nucleosomes and maintain chromatin homeostasis.
Keywords: Chaperone; HIstone chaperone; Nucleosome; chromatin; histones.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Fly Fishing for Histones: Catch and Release by Histone Chaperone Intrinsically Disordered Regions and Acidic Stretches.J Mol Biol. 2017 Aug 4;429(16):2401-2426. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2017.06.005. Epub 2017 Jun 10. J Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28610839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Characterization of Histone Chaperones using Analytical, Pull-Down and Chaperoning Assays.J Vis Exp. 2021 Dec 29;(178). doi: 10.3791/63218. J Vis Exp. 2021. PMID: 35037657
-
Histone chaperone networks shaping chromatin function.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017 Mar;18(3):141-158. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2016.159. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28053344 Free PMC article. Review.
-
All roads lead to chromatin: multiple pathways for histone deposition.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Mar-Apr;1819(3-4):238-46. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 24459726 Review.
-
Histones, histone chaperones and nucleosome assembly.Protein Cell. 2010 Jul;1(7):607-12. doi: 10.1007/s13238-010-0086-y. Protein Cell. 2010. PMID: 21203931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Protein acetylation: a novel modus of obesity regulation.J Mol Med (Berl). 2021 Sep;99(9):1221-1235. doi: 10.1007/s00109-021-02082-2. Epub 2021 Jun 1. J Mol Med (Berl). 2021. PMID: 34061242 Review.
-
The nucleic acid binding protein SFPQ represses EBV lytic reactivation by promoting histone H1 expression.Nat Commun. 2024 May 16;15(1):4156. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48333-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38755141 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of histone-binding proteins with multi-angle light scattering.Methods. 2020 Dec 1;184:93-101. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2020.01.014. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Methods. 2020. PMID: 31988003 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Bioinformatic Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes Associated with Wound Healing.Cell J. 2023 Dec 31;25(12):874-882. doi: 10.22074/cellj.2023.2007217.1368. Cell J. 2023. PMID: 38192258 Free PMC article.
-
DNAJC9 integrates heat shock molecular chaperones into the histone chaperone network.Mol Cell. 2021 Jun 17;81(12):2533-2548.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.03.041. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Mol Cell. 2021. PMID: 33857403 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

