K27-linked ubiquitination of BRAF by ITCH engages cytokine response to maintain MEK-ERK signaling
- PMID: 31015455
- PMCID: PMC6478693
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-09844-0
K27-linked ubiquitination of BRAF by ITCH engages cytokine response to maintain MEK-ERK signaling
Abstract
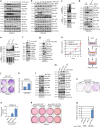
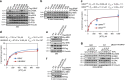
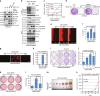
BRAF plays an indispensable role in activating the MEK/ERK pathway to drive tumorigenesis. Receptor tyrosine kinase and RAS-mediated BRAF activation have been extensively characterized, however, it remains undefined how BRAF function is fine-tuned by stimuli other than growth factors. Here, we report that in response to proinflammatory cytokines, BRAF is subjected to lysine 27-linked poly-ubiquitination in melanoma cells by the ITCH ubiquitin E3 ligase. Lysine 27-linked ubiquitination of BRAF recruits PP2A to antagonize the S365 phosphorylation and disrupts the inhibitory interaction with 14-3-3, leading to sustained BRAF activation and subsequent elevation of the MEK/ERK signaling. Physiologically, proinflammatory cytokines activate ITCH to maintain BRAF activity and to promote proliferation and invasion of melanoma cells, whereas the ubiquitination-deficient BRAF mutant displays compromised kinase activity and reduced tumorigenicity. Collectively, our study reveals a pivotal role for ITCH-mediated BRAF ubiquitination in coordinating the signals between cytokines and the MAPK pathway activation in melanoma cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

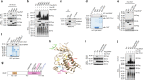


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

