Formulation design, characterization, and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of nanostructured lipid carriers containing a bile salt for oral delivery of gypenosides
- PMID: 31015758
- PMCID: PMC6448534
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S194934
Formulation design, characterization, and in vitro and in vivo evaluation of nanostructured lipid carriers containing a bile salt for oral delivery of gypenosides
Abstract
Background: Gypenosides (GPS) have been used as traditional medicine for centuries with various pharmacological effects. However, its therapeutic effects were restricted owing to the poor lipid and water solubility and low absorption. This study aimed to develop nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs) containing a bile salt formulation (sodium glycocholate, SGC) for GPS, and to evaluate the potential of the GPS-SGC-NLCs as an oral delivery system.
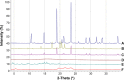
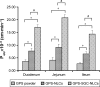
Methods: The preparation of GPS-SGC-NLCs was investigated using a single-factor test and a central composite design of response surface methodology. In vitro release and pharmacokinetics studies were used to evaluate the dissolution and bioavailability of GPS. Furthermore, In vivo imaging and in situ intestinal perfusion studies were performed to investigate the absorption of the preparations in the gastrointestinal tract.
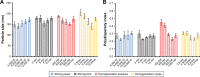
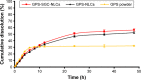
Results: The optimised formulation yielded nanoparticles with an approximate diameter of 146.7 nm, polydispersity of 0.137, zeta potential of -56.0 mV, entrapment efficiency of 74.22% and drug loading of 4.89%. An in vitro dissolution analysis revealed the sustained release of contents from GPS-SGC-NLCs over 48 h with 56.4% of the drug released. A pharmacokinetic analysis revealed an 8.5-fold increase of bioavailability of the GPS-SGC-NLCs compared with GPS powder. In vivo imaging and in situ intestinal perfusion studies showed that SGC-NLCs could significantly increase the absorption of GPS in intestinal tract. In vitro cytotoxicity evaluated using Caco-2 cells demonstrated that GPS-SGC-NLCs decrease the cytotoxicity of the drug.
Conclusion: The SGC-NLC formulation can significantly improve the absorption of GPS, which provides an effective approach for enhancing the oral absorption of drugs.
Keywords: bile salt; bioavailability; gypenosides; in vitro release; nanostructured lipid carriers.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Size-exclusive effect of nanostructured lipid carriers on oral drug delivery.Int J Pharm. 2016 Sep 10;511(1):524-537. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2016.07.049. Epub 2016 Jul 22. Int J Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27452421
-
Preparation and characterization of nimodipine-loaded nanostructured lipid systems for enhanced solubility and bioavailability.Int J Nanomedicine. 2018 Dec 21;14:119-133. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S186899. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2018. PMID: 30613141 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation, characterization and pharmacokinetic studies of linalool-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers.Pharm Biol. 2016 Oct;54(10):2320-8. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2016.1155630. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Pharm Biol. 2016. PMID: 26986932
-
Nanostructured lipid (NLCs) carriers as a bioavailability enhancement tool for oral administration.Drug Deliv. 2015;22(6):691-700. doi: 10.3109/10717544.2014.898110. Epub 2014 Mar 27. Drug Deliv. 2015. PMID: 24670099 Review.
-
Nose to Brain: Exploring the Progress of Intranasal Delivery of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Nanostructured Lipid Carriers.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Nov 21;19:12343-12368. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S497480. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39606563 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Methotrexate-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carrier Gel Alleviates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis by Moderating Inflammation: Formulation, Optimization, Characterization, In-Vitro and In-Vivo Studies.Int J Nanomedicine. 2020 Jul 7;15:4763-4778. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S247007. eCollection 2020. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020. PMID: 32753865 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Nanostructured Lipid Carriers and its Application in Drug Delivery through Different Routes.Adv Pharm Bull. 2023 Jul;13(3):446-460. doi: 10.34172/apb.2023.056. Epub 2022 Sep 18. Adv Pharm Bull. 2023. PMID: 37646052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanostructured Lipid Carrier-Mediated Transdermal Delivery of Aceclofenac Hydrogel Present an Effective Therapeutic Approach for Inflammatory Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 20;12:713616. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.713616. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34616297 Free PMC article.
-
Stabilized oral nanostructured lipid carriers of Adefovir Dipivoxil as a potential liver targeting: Estimation of liver function panel and uptake following intravenous injection of radioiodinated indicator.Daru. 2020 Dec;28(2):517-532. doi: 10.1007/s40199-020-00355-8. Epub 2020 Jun 20. Daru. 2020. PMID: 32564282 Free PMC article.
-
Ezetimibe-Loaded Nanostructured Lipid Carrier Based Formulation Ameliorates Hyperlipidaemia in an Experimental Model of High Fat Diet.Molecules. 2021 Mar 9;26(5):1485. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051485. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33803259 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shi L, Pi Y, Luo C, Zhang C, Tan D, Meng X. In vitro inhibitory activities of six gypenosides on human liver cancer cell line HepG2 and possible role of HIF-1α pathway in them. Chem Biol Interact. 2015;238:48–54. - PubMed
-
- Mu R-H, Fang X-Y, Wang S-S, et al. Antidepressant-like effects of standardized gypenosides: involvement of brain-derived neu-rotrophic factor signaling in hippocampus. Psychopharmacology. 2016;233(17):3211–3221. - PubMed
-
- Chen M-H, Chen S-H, Wang Q-F, et al. The molecular mechanism of gypenosides-induced G1 growth arrest of rat hepatic stellate cells. J Ethnopharmacol. 2008;117(2):309–317. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

