Multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Canada, 2012-2016
- PMID: 31015818
- PMCID: PMC6461123
- DOI: 10.14745/ccdr.v45i23a01
Multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Canada, 2012-2016
Abstract
Background: Neisseria gonorrhoeae have acquired resistance to many antimicrobials, including third generation cephalosporins and azithromycin, which are the current gonococcal combination therapy recommended by the Canadian Guidelines on Sexually Transmitted Infections.
Objective: To describe antimicrobial susceptibilities for N. gonorrhoeae circulating in Canada between 2012 and 2016.
Methods: Antimicrobial resistance profiles were determined using agar dilution of N. gonorrhoeae isolated in Canada 2012-2016 (n=10,167) following Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute guidelines. Data were analyzed by applying multidrug-resistant gonococci (MDR-GC) and extensively drug-resistant gonococci (XDR-GC) definitions.
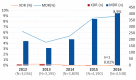
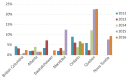
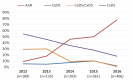
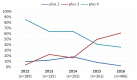
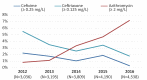
Results: Between 2012 and 2016, the proportion of MDR-GC increased from 6.2% to 8.9% and a total of 19 cases of XDR-GC were identified in Canada (0.1%, 19/18,768). The proportion of isolates with decreased susceptibility to cephalosporins declined between 2012 and 2016 from 5.9% to 2.0% while azithromycin resistance increased from 0.8% to 7.2% in the same period.
Conclusion: While XDR-GC are currently rare in Canada, MDR-GC have increased over the last five years. Azithromycin resistance in N. gonorrhoeae is established and spreading in Canada, exceeding the 5% level at which the World Health Organization states an antimicrobial should be reviewed as an appropriate treatment. Continued surveillance of antimicrobial susceptibilities of N. gonorrhoeae is necessary to inform treatment guidelines and mitigate the impact of resistant gonorrhea.
Keywords: N. gonorrhoeae multidrug resistant; Neisseria gonorrhoeae; antimicrobial resistance; laboratory surveillance.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None.
Figures

References
-
- Public Health Agency of Canada. Reported cases from 1991 to 2016 in Canada - Notifiable diseases on-line. Ottawa (ON): Government of Canada; 2017. http://diseases.canada.ca/notifiable/charts?c=yl
-
- Newman L, Rowley J, Vander Hoorn S, Wijesooriya NS, Unemo M, Low N, Stevens G, Gottlieb S, Kiarie J, Temmerman M. Global estimates of the prevalence and incidence of four curable sexually transmitted infections in 2012 based on systematic review and global reporting. PLoS One 2015. Dec;10(12):e0143304. .10.1371/journal.pone.0143304 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Public Health Agency of Canada. National Surveillance of Antimicrobial Susceptibilities of Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Canada - Annual Summary 2016. Ottawa (ON): Government of Canada; 2018. https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/publications/drugs-healt...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous