Effect of Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) in Pulmonary Inflammation in Asthma Induced by House Dust Mite (HDM): Dosimetry Study
- PMID: 31015955
- PMCID: PMC6448342
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/3945496
Effect of Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) in Pulmonary Inflammation in Asthma Induced by House Dust Mite (HDM): Dosimetry Study
Abstract
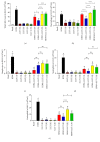
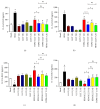
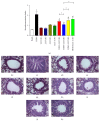
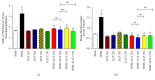
Asthma is characterized by chronic inflammation in the airways. Several models have been proposed for the discovery of new therapies. Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT) is relatively new and effective, very low cost, with no side effects. However, there is still no consensus on the optimal dose to be used. In this sense, the objective of the present study was to evaluate the best dose in an experimental model of asthma induced by House Dust Mite (HDM). Balb/c mice received administration of 100 ug/animal HDM and LLLT applications (diode laser: 660 nm, 100 mW and four different energies 1J, 3J, 5J, and 7.5J) for 16 days. After 24 hours, we studied inflammatory, functional, and structural parameters. The results showed that LBI was able to modulate the pulmonary inflammation observed by reducing the number of cells in Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid (BALF) as well as reducing the percentage of neutrophils, eosinophils and T lymphocytes. On the other hand, LLLT increased the level of IL-10 and reduced levels of IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 in BALF. LLLT was able to reduce the production of mucus, peribronchial eosinophils, collagen deposition, bronchoconstriction index, and bronchial and muscular thickening in the airways. We concluded that the use of LLLT in the treatment of chronic inflammation of the airways attenuated the inflammatory process and functional and structural parameters. We emphasize, in general, that the 1J and 3J laser presented better results. Thus, photobiomodulation may be considered a promising tool for the treatment of chronic pulmonary allergic inflammation observed in asthma.
Figures



References
-
- GINA. Global Initiative for Asthma. Strategy for Asthma management and prevention, 2018, http://www.ginaasthma.org.
-
- Mikhailov V. A., Aleksandrova O., Gol'dina E. M. The immunomodulating action of low-energy laser radiation in the treatment of bronchial asthma. Voprosy Kurortologii, Fizioterapii, I Lechebnoĭ Fizicheskoĭ Kultury. 1998;4:23–25. - PubMed
-
- Carvalho J. L., Britto A., de Oliveira A. P. L., et al. Beneficial effect of low-level laser therapy in acute lung injury after i-I/R is dependent on the secretion of IL-10 and independent of the TLR/MyD88 signaling. Lasers in Medical Science. 2017;32(2):305–315. doi: 10.1007/s10103-016-2115-4. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

