Validation of POSSUM, P-POSSUM and the surgical risk scale in major general surgical operations in Harare: A prospective observational study
- PMID: 31016016
- PMCID: PMC6475666
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2019.03.007
Validation of POSSUM, P-POSSUM and the surgical risk scale in major general surgical operations in Harare: A prospective observational study
Abstract
Background: Raw mortality and morbidity, though commonly studied in surgical audit can nonetheless be misleading because of differences in preoperative and intraoperative findings of patients. There are some common scoring systems specifically designed to cater for case mix but these have not been tried locally. This study sought to validate these scoring systems and hopefully adopt them for our teaching hospitals.
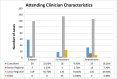
Materials and methods: A prospective observational cohort study was conducted at two central hospitals in Harare Two hundred and two patients undergoing a variety of major general surgical operations were recruited into the study. Results of physiological and intraoperative parameters collected from the patients' records were scored according to POSSUM, P-POSSUM and SRS scores. Predicted mortality and morbidity rates of all these subjects were then compared to the observed rates.
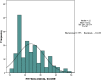
Results: One hundred and eighty one patients participated (123 males, 58 females). Using the POSSUM morbidity score, the observed versus expected (O: E) ratio of 0.88 showed no difference (p = 0.970). Using POSSUM, P-POSSUM and SRS mortality scores, O: E ratios of 0.74, 1.06 and 1.0 respectively were obtained, the differences were not significant (p = 0.650, p = 0.987 and 0.730). All three scores were comparable on the Receiver Operating Characteristic curve. The Physiological score independently predicted mortality (p < 0.00001).
Conclusion: POSSUM, P-POSSUM and SRS scores are comparable and suitable for estimating outcomes after major surgery in Harare. A larger study inclusive of low risk patients is needed to generalise these findings across Zimbabwean patients.
Keywords: ASA, American Society of Anesthesiologists; Audit; P-POSSUM, Portsmouth-POSSUM; POSSUM; POSSUM, Physiological and Operative Severity Scoring for the enUmeration of Mortality and Morbidity; Risk scoring system; SRS, Surgical Risk Scale.
Figures
References
-
- Surgical Audit and Peer Review . vol. 3. 2008. A Guide by the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons; pp. 2–46.www.surgeons.org/publications
-
- Ghaferi A.A., Birkmeyer J.D., Dimick J.B. Variation in hospital mortality associated with inpatient surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009;361:1368–1375. - PubMed
-
- Copeland G.P., Jones D., Walters M. POSSUM: a scoring system for surgical audit. Br. J. Surg. 1991;78:355–360. - PubMed
-
- Whiteley M.S., Prytherch D.R., Higgins B., Weaver P.C., Prout W.G. An evaluation of the POSSUM surgical scoring system. Br. J. Surg. 1996;83:812–815. - PubMed
-
- Prytherch D.R., Whiteley M.S., H B. POSSUM and Portsmouth POSSUM for predicting mortality. Physiological and operative severity score for the enUmeration of mortality and morbidity. Br. J. Surg. 1998;85(9):1217–1220. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources