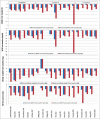
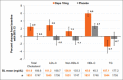
Sodium Glucose Co-transporter-2 Inhibitor: Benefits beyond Glycemic Control
- PMID: 31016169
- PMCID: PMC6446679
- DOI: 10.4103/ijem.IJEM_160_17
Sodium Glucose Co-transporter-2 Inhibitor: Benefits beyond Glycemic Control
Abstract
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a family of metabolic disorders characterized by hyperglycemia as a consequence of abnormalities in insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity. It affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide and leads to increased morbidity, compromised quality of life, higher mortality sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, a new class of oral antidiabetic drugs, have garnered considerable attention in the recent past and are considered potential first-line candidates for the management of T2DM. This review outlines the evidence-based therapeutic efficacy, safety, limitations, and advantages of SGLT2 inhibitors in the management of T2DM. SGLT2 inhibitors work by preventing the kidneys from reabsorbing glucose back into the blood, leading to increase in excretion of glucose through urine, thereby lowering hyperglycemia. Treatment with SGLT2 inhibitors improves A1C levels, reduces blood pressure and body weight, and is overall well tolerated by patients with T2DM. However, additional data on long-term cardiovascular safety are still needed. Characteristic adverse events include mild genital - urinary tract infection more commonly seen in women than in men, but serious infection is uncommon. Their use should be exercised with extra caution in patients suffering from renal impairment. Further, advancing to dual/triple combinational therapies with SGLT2 inhibitors and existing oral antidiabetic options may prove to be a breakthrough in the management of T2DM.
Keywords: Efficacy; Type 2 diabetes mellitus; hyperglycemia; safety; sodium glucose co-transporter Type 2 inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacodynamics, efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose co-transporter type 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.Drugs. 2015 Jan;75(1):33-59. doi: 10.1007/s40265-014-0337-y. Drugs. 2015. PMID: 25488697 Review.
-
The Role of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes.Clin Ther. 2015 Jun 1;37(6):1150-66. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2015.03.004. Epub 2015 Apr 16. Clin Ther. 2015. PMID: 25891804 Review.
-
Sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: a growing class of antidiabetic agents.Drugs Context. 2014 Dec 19;3:212264. doi: 10.7573/dic.212264. eCollection 2014. Drugs Context. 2014. PMID: 25598831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of antidiabetic drugs on the incidence of macrovascular complications and mortality in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a new perspective on sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors.Ann Med. 2017 Feb;49(1):51-62. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2016.1226514. Epub 2016 Sep 22. Ann Med. 2017. PMID: 27535028 Review.
-
Update on developments with SGLT2 inhibitors in the management of type 2 diabetes.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014 Sep 11;8:1335-80. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S50773. eCollection 2014. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2014. PMID: 25246775 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The novel role of Periploca laevigata Aiton extracts as antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory functions in pancreatic Β cells exposed to hyperglycaemia.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025 Jun 2;24(1):136. doi: 10.1007/s40200-025-01654-0. eCollection 2025 Jun. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2025. PMID: 40469912
-
Impact of SGLT2 inhibitors on myocardial fibrosis in diabetic HFpEF: a longitudinal study.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jul 8;30(1):592. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02834-7. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40624547 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Anemia of Chronic Kidney Disease-A Narrative Review of Its Pathophysiology, Diagnosis, and Management.Biomedicines. 2024 May 27;12(6):1191. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061191. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A retrospective analysis of the incidence, outcome and factors associated with the occurrence of euglycemic ketoacidosis in diabetic patients on sodium glucose co-transporter - 2 inhibitors undergoing cardiac surgery.Ann Card Anaesth. 2022 Oct-Dec;25(4):460-465. doi: 10.4103/aca.aca_47_21. Ann Card Anaesth. 2022. PMID: 36254911 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Atrial Fibrillation Recurrence after Catheter Ablation in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Reconstructed Kaplan-Meier Curves with Trial Sequential Analysis.Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2024 Sep;24(5):629-640. doi: 10.1007/s40256-024-00661-5. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38963527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson JH, Jr, Brunelle RL, Koivisto VA, Trautmann ME, Vignati L, DiMarchi R. Improved mealtime treatment of diabetes mellitus using an insulin analogue. Multicenter Insulin Lispro Study Group. Clin Ther. 1997;19:62–72. - PubMed
-
- Anjana RM, Pradeepa R, Deepa M, Datta M, Sudha V, Unnikrishnan R, et al. Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes (impaired fasting glucose and/or impaired glucose tolerance) in urban and rural India: Phase I results of the Indian Council of Medical Research-INdia DIABetes (ICMR-INDIAB) study. Diabetologia. 2011;54:3022–7. - PubMed
-
- Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, Blonde L, Bloomgarden ZT, Bush MA, et al. Consensus statement by the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American College of Endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm-2016 executive summary. Endocr Pract. 2016;22:84–113. - PubMed
-
- Kumpatla S, Kothandan H, Tharkar S, Viswanathan V. The costs of treating long-term diabetic complications in a developing country: A study from India. J Assoc Physicians India. 2013;61:102–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous