An Inulin-Specific Lectin with Anti-HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase, Antiproliferative, and Mitogenic Activities from the Edible Mushroom Agaricus bitorquis
- PMID: 31016184
- PMCID: PMC6444243
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/1341370
An Inulin-Specific Lectin with Anti-HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase, Antiproliferative, and Mitogenic Activities from the Edible Mushroom Agaricus bitorquis
Abstract
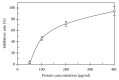
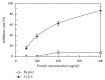
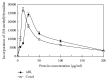
A novel lectin (ABL) was purified from the dried fruiting bodies of Agaricus bitorquis. An efficient 3-step purification protocol involved two consecutive steps of ion exchange chromatography on Q-Sepharose and SP-Sepharose and gel filtration by FPLC on Superdex 75. ABL is a monomeric protein with the molecular mass of 27.6 kDa, which is different from other lectins from genus Agaricus. Its N-terminal amino acid sequence is EYTISIRVYQTNPKGFNRPV which is unique and sharing considerably high similarity of other mushroom lectins. The hemagglutinating activity of the lectin was inhibited by inulin. Based on hemagglutination tests, ABL prefers rabbit, human type A, and AB erythrocytes to human type B and O erythrocytes. The lectin inhibits the activity of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase and the proliferation of leukemia cell (L1210) with an IC50 value of 4.69 and 4.97 μM, respectively. Furthermore, ABL demonstrates the highest mitogenic activity with a response of 24177.7 ± 940.6 [3H-methyl] thymidine counts per minute (CPM) at a concentration of 0.91 μM.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A novel lectin with potent antitumor, mitogenic and HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitory activities from the edible mushroom Pleurotus citrinopileatus.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Jan;1780(1):51-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2007.09.004. Epub 2007 Sep 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 17961926
-
Isolation and characterization of a novel lectin from the edible mushroom Stropharia rugosoannulata.Molecules. 2014 Nov 28;19(12):19880-91. doi: 10.3390/molecules191219880. Molecules. 2014. PMID: 25460311 Free PMC article.
-
A novel lectin with highly potent antiproliferative and HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitory activities from the edible wild mushroom Russula delica.Glycoconj J. 2010 Feb;27(2):259-65. doi: 10.1007/s10719-009-9274-5. Glycoconj J. 2010. PMID: 20187295
-
Lectins from the Edible Mushroom Agaricus bisporus and Their Therapeutic Potentials.Molecules. 2020 May 20;25(10):2368. doi: 10.3390/molecules25102368. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32443732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mushroom lectins in biomedical research and development.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 May 15;151:1340-1350. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.10.180. Epub 2019 Nov 18. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 31751693 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioactive Peptides and Other Immunomodulators of Mushroom Origin.Biomedicines. 2024 Jul 4;12(7):1483. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12071483. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39062056 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Narrative Review: Bioactive Potential of Various Mushrooms as the Treasure of Versatile Therapeutic Natural Product.J Fungi (Basel). 2021 Sep 6;7(9):728. doi: 10.3390/jof7090728. J Fungi (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34575766 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lectins Are the Sparkle of Hope for Combating Coronaviruses and the Global COVID-19.Adv Pharm Bull. 2022 Mar;12(2):319-328. doi: 10.34172/apb.2022.030. Epub 2021 Mar 27. Adv Pharm Bull. 2022. PMID: 35620331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Screening of mushrooms from the woodlands of Zimbabwe: Occurrence of lectins and partial purification of a mucin specific lectin from Boletus edulis.PLoS One. 2022 Apr 14;17(4):e0265494. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265494. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35421104 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory Effects of Edible and Medicinal Mushrooms and Their Bioactive Immunoregulatory Products.J Fungi (Basel). 2020 Nov 8;6(4):269. doi: 10.3390/jof6040269. J Fungi (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33171663 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

