Effects of Resveratrol on the Mechanisms of Antioxidants and Estrogen in Alzheimer's Disease
- PMID: 31016201
- PMCID: PMC6446083
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/8983752
Effects of Resveratrol on the Mechanisms of Antioxidants and Estrogen in Alzheimer's Disease
Abstract
Objective: To observe the effects of resveratrol (Res) on the antioxidative function and estrogen level in an Alzheimer's disease (AD) mouse model.
Methods: First, we examined the effects of Res on an AD mice model. SAMP8 mice were selected as the model, and normal-aging SAMR1 mice were used as the control group. The model mice were randomly divided into three groups: a model group, high-dose Res group (40mg/kg, intraperitoneal (ip)), and low-dose Res group (20mg/kg, ip). After receiving medication for 15 days, the mice were subjected to the water maze test to assess their spatial discrimination. The spectrophotometric method was used to detect the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), and catalase (CAT) as well as the malondialdehyde (MDA) content. Quantitative PCR (q-PCR) was used to detect SOD, GSH-Px, CAT, and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) mRNA level changes. Western blot analysis detected HO-1 and Nrf2 protein expression. Second, we researched the effect of Res on the estrogen level in the SAMP8 model mice. The model mice were randomly divided into four groups: a model group, estrogen replacement group (0.28 mg/kg, intramuscular (im), estradiol benzoate), high-dose Res group (5 mg/kg, im), and low-dose Res group (2.5 mg/kg, im). The mice were injected, once every three days, for 5 weeks. Q-PCR was used to detect brain tissue mRNA expression changes. Western blot analysis detected ERα, ERβ, and ChAT protein expression. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit was used to detect the expression of E2 and amyloid β protein (Aβ) in brain tissue.
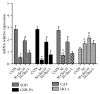
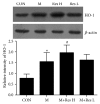
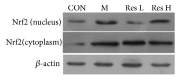
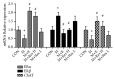
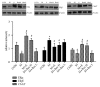
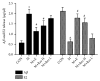
Results: Compared with the control treatment, Res could improve the spatial abilities of the mice to a certain extent and also increase the expression of SOD, GSH-Px, CAT, and HO-1 at the mRNA level (P<0.05). In addition, enhanced SOD, GSH-Px, and CAT activities and HO-1 protein levels and decreased MDA content (P<0.05) were detected in the brain tissue of the Res-treated mice. The cytoplasmic Nrf2 content in the Res-treated mice was also decreased while the nuclear Nrf2 content and the nuclear translation rate of Nrf2 were increased (P<0.05). Res could decrease the expression of ERβ in the brain tissue at the mRNA and protein levels and the expression of Aβ in the brain tissue at the protein level. Res could also increase the mRNA and protein expression of ERα and ChAT and the protein expression of estradiol in the brain tissue.
Conclusion: Res can increase the antioxidant capacity of AD models through the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. In addition, Res can enhance estrogen levels in an AD model. These findings provide a new idea for the treatment of AD.
Figures
References
-
- Na L., Cheng X., Qian W., et al. Resveratrol inhibits hippocampal β-APP expression and improves learning and memory in rats. Chinese Journal of Public Health. 2015;3:p. 022.
-
- Liang C., Chuan Q. The role of microRNA in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Chinese Journal of Comparative Medicine. 2011;21(6):75–79.
-
- Zhang L., Wang C., Bo L., et al. Effect of resveratrol on oxidative stress injury of central nervous system in obstructive jaundice rats. Chinese Journal of Basic Surgery and Clinical Medicine. 2016;(1):42–47.
-
- Yang Z., Yan L., Yuan S. Oxidative stress and Alzheimer's disease. Life Science Research. 2015;19:265–275.
-
- Liu X., Wei Y., Qi J. Oxidative stress and Alzheimer's disease. Journal of Physiology. 2012;64(1):87–95. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

