Maternal Immune Activation during Pregnancy Alters the Behavior Profile of Female Offspring of Sprague Dawley Rats
- PMID: 31016229
- PMCID: PMC6477592
- DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0437-18.2019
Maternal Immune Activation during Pregnancy Alters the Behavior Profile of Female Offspring of Sprague Dawley Rats
Abstract
Sex differences are documented in psychiatric and neurological disorders, yet most preclinical animal research has been conducted in males only. There is a need to better understand of the nature of sex differences in brain disease in order to meet the needs of psychiatric patients. We present the behavior profile of adult female offspring produced using a maternal immune activation (MIA) model where pregnant rats receive an immune stimulant and the offspring typically show various abnormalities consistent with psychiatric illnesses such as schizophrenia and autism. The results in female offspring were compared to a previously published cohort of their male siblings (Lins et al., 2018). We examined prepulse inhibition (PPI), sociability, MK-801-induced locomotor activity, crossmodal object recognition (CMOR), and oddity discrimination; behaviors relevant to the positive, negative, and cognitive symptoms of schizophrenia. No between-treatment differences in PPI or locomotor activity were noted. Tactile memory was observed in the control and treated female offspring, visual recognition memory was deficient in the polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid (polyI:C) offspring only, and both groups lacked crossmodal recognition. PolyI:C offspring were impaired in oddity preference and had reduced preference for a stranger conspecific in a sociability assay. Systemic maternal CXCL1, IL-6, and TNF-a levels 3 h after polyI:C treatment were determined, but no relationship was found between these cytokines and the behavior seen in the adult female offspring. Overall, female offspring of polyI:C-treated dams display an array of behavior abnormalities relevant to psychiatric illnesses such as schizophrenia similar to those previously reported in male rats.
Keywords: behavior; prepulse inhibition; recognition memory; sex differences; sociability.
Figures
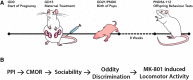

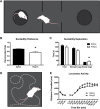
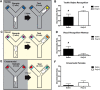
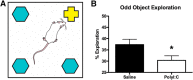
Comment in
-
Does Prenatal Exposure to Maternal Inflammation Causes Sex Differences in Schizophrenia-Related Behavioral Outcomes in Adult Rats?eNeuro. 2019 Nov 12;6(6):ENEURO.0393-19.2019. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0393-19.2019. Print 2019 Nov/Dec. eNeuro. 2019. PMID: 31719107 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Prospective Analysis of the Effects of Maternal Immune Activation on Rat Cytokines during Pregnancy and Behavior of the Male Offspring Relevant to Schizophrenia.eNeuro. 2018 Aug 29;5(4):ENEURO.0249-18.2018. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0249-18.2018. eCollection 2018 Jul-Aug. eNeuro. 2018. PMID: 30225350 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral alterations in rat offspring following maternal immune activation and ELR-CXC chemokine receptor antagonism during pregnancy: implications for neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015 Mar 3;57:155-65. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.11.002. Epub 2014 Nov 12. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25445065 Free PMC article.
-
Altered object-in-place recognition memory, prepulse inhibition, and locomotor activity in the offspring of rats exposed to a viral mimetic during pregnancy.Neuroscience. 2012 Jan 10;201:184-98. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2011.11.011. Epub 2011 Nov 11. Neuroscience. 2012. PMID: 22119062 Free PMC article.
-
Towards an immuno-precipitated neurodevelopmental animal model of schizophrenia.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2005;29(6):913-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2004.10.012. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2005. PMID: 15964075 Review.
-
Schizophrenia: do all roads lead to dopamine or is this where they start? Evidence from two epidemiologically informed developmental rodent models.Transl Psychiatry. 2012 Feb 21;2(2):e81. doi: 10.1038/tp.2012.6. Transl Psychiatry. 2012. PMID: 22832818 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Influence of Prenatal Drug Exposure, Maternal Inflammation, and Parental Aging on the Development of Autism Spectrum Disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Feb 9;13:821455. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.821455. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 35222122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maternal immune activation as a risk factor for psychiatric illness in the context of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021 Oct;16:100297. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100297. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021. PMID: 34308388 Free PMC article.
-
Does Prenatal Exposure to Maternal Inflammation Causes Sex Differences in Schizophrenia-Related Behavioral Outcomes in Adult Rats?eNeuro. 2019 Nov 12;6(6):ENEURO.0393-19.2019. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0393-19.2019. Print 2019 Nov/Dec. eNeuro. 2019. PMID: 31719107 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal Immune Activation with the Viral Mimetic Poly:IC in Pregnant Rats.Bio Protoc. 2020 Nov 20;10(22):e3817. doi: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3817. eCollection 2020 Nov 20. Bio Protoc. 2020. PMID: 33659469 Free PMC article.
-
Maternal choline supplementation modulates cognition and induces anti-inflammatory signaling in the prefrontal cortices of adolescent rats exposed to maternal immune activation.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024 Aug 3;40:100836. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2024.100836. eCollection 2024 Oct. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2024. PMID: 39206430 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andiné P, Widermark N, Axelsson R, Nyberg G, Olofsson U, Mårtensson E, Sandberg M (1999) Characterization of MK-801-induced behavior as a putative rat model of psychosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 290:1393–1408. - PubMed
-
- Arad M, Piontkewitz Y, Albelda N, Shaashua L, Weiner I (2017) Immune activation in lactating dams alters sucklings’ brain cytokines and produces non-overlapping behavioral deficits in adult female and male offspring: a novel neurodevelopmental model of sex-specific psychopathology. Brain Behav Immun 63:35–49. 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.01.015 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ballendine SA, Greba Q, Dawicki W, Zhang X, Gordon JR, Howland JG (2015) behavioral alterations in rat offspring following maternal immune activation and ELR-CXC chemokine receptor antagonism during pregnancy: implications for neurodevelopmental psychiatric disorders. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 57:155–165. 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.11.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
