Ablation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor promotes angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis through enhanced c-Jun/HIF-1α signaling
- PMID: 31016362
- PMCID: PMC7395242
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-019-02446-1
Ablation of aryl hydrocarbon receptor promotes angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis through enhanced c-Jun/HIF-1α signaling
Abstract
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) is a transcription factor that binds to DNA as a heterodimer with the AHR nuclear translocator (ARNT) after interaction with ligands, such as polycyclic and halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons and other xenobiotics. The endogenous ligands and functions of AHR have been the subject of many investigations. In the present study, the potential role of AHR signaling in the development of left ventricular hypertrophy and cardiac fibrosis by angiotensin II (Ang II) infusion was investigated in mice lacking the AHR gene (Ahr-/-). We also assessed the hypothesis that fenofibrate, a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPARα) activator, reduces cardiac fibrosis through the c-Jun signaling. Male Ahr-/- and age-matched wild-type mice (n = 8 per group) were infused with Ang II at 100 ng/kg/min daily for 2 weeks. Treatment with Ang II increased systolic blood pressure to comparable levels in Ahr-/- and wild-type mice. However, Ahr-/- mice developed severe cardiac fibrosis after Ang II infusion compared with wild-type mice. Ang II infusion also significantly increased the expression of endothelin in the left ventricles of Ahr-/- mice, but not in wild-type mice, and significantly increased the c-Jun signaling in Ahr-/- mice. Ang II infusion also significantly enhanced the expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and the downstream target vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the left ventricles of Ahr-/- mice. These results suggested pathogenic roles for the AHR signaling pathway in the development of cardiac fibrosis. Treatment with fenofibrate reduced cardiac fibrosis and abrogated the effects of Ang II on the expression of endothelin, HIF-1α, and VEGF. The inhibitory effect of fenofibrate on cardiac fibrosis was mediated by suppression of VEGF expression through modulation of c-Jun/HIF-1α signaling.
Keywords: AHR; Angiotensin II; Cardiac hypertrophy; Fibrosis; HIF-1α; PPARα; Vascular endothelial growth factor.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
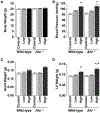

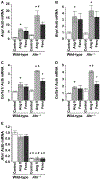



References
-
- Balakumar P, Rohilla A, Mahadevan N (2011) Pleiotropic actions of fenofibrate on the heart. Pharmacol Res 63:8–12 - PubMed
-
- Carreira VS, Fan Y, Kurita H, Wang Q, Ko CI, Naticchioni M, Jiang M, Koch S, Zhang X, Biesiada J, Medvedovic M, Xia Y, Rubinstein J, Puga A (2015) Disruption of Ah receptor signaling during mouse development leads to abnormal cardiac structure and function in the adult. PLoS One 10:e0142440. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Duhaney TA, Cui L, Rude MK, Lebrasseur NK, Ngoy S, De Silva DS, Siwik DA, Liao R, Sam F (2007) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha-independent actions of fenofibrate exac-erbates left ventricular dilation and fibrosis in chronic pressure overload. Hypertension 49:1084–1094 - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Salguero P, Pineau T, Hilbert DM, McPhail T, Lee SS, Kim S, Nebert DW, Rudikoff S, Ward JM, Gonzalez FJ (1995) Immune system impairment and hepatic fibrosis in mice lacking the dioxin-binding Ah receptor. Science 268:722–726 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

