Real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification: an early-warning tool for quarantine plant pathogen detection
- PMID: 31016406
- PMCID: PMC6478783
- DOI: 10.1186/s13568-019-0774-9
Real-time loop-mediated isothermal amplification: an early-warning tool for quarantine plant pathogen detection
Abstract
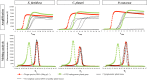
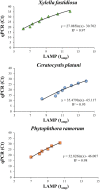
An effective framework for early warning and rapid response is a crucial element to prevent or mitigate the impact of biological invasions of plant pathogens, especially at ports of entry. Molecular detection of pathogens by using PCR-based methods usually requires a well-equipped laboratory. Rapid detection tools that can be applied as point-of-care diagnostics are highly desirable, especially to intercept quarantine plant pathogens such as Xylella fastidiosa, Ceratocystis platani and Phytophthora ramorum, three of the most devastating pathogens of trees and ornamental plants in Europe and North America. To this aim, in this study we developed three different loop mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assays able to detect each target pathogen both in DNA extracted from axenic culture and in infected plant tissues. By using the portable instrument Genie® II, the LAMP assay was able to recognize X. fastidiosa, C. platani and P. ramorum DNA within 30 min of isothermal amplification reaction, with high levels of specificity and sensitivity (up to 0.02 pg µL-1 of DNA). These new LAMP-based tools, allowing an on-site rapid detection of pathogens, are especially suited for being used at ports of entry, but they can be also profitably used to monitor and prevent the possible spread of invasive pathogens in natural ecosystems.
Keywords: Alien pathogens; Canker Stain Disease; Isothermal amplification; LAMP; Olive Quick Decline Syndrome; Portable diagnostics; Sudden Oak Death.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification Detection of Phytophthora kernoviae, P. ramorum, and the P. ramorum NA1 Lineage on a Microfluidic Chip and Smartphone Platform.Phytopathology. 2025 Feb;115(2):192-203. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-02-24-0055-R. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Phytopathology. 2025. PMID: 39434003
-
Real-Time Portable LAMP Assay for a Rapid Detection of Xylella fastidiosa In-Field.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2659:51-60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3159-1_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37249884
-
Multiplex LAMP Detection of the Genus Phytophthora and Four Phytophthora Species P. ramorum, P. lateralis, P. kernoviae, and P. nicotianae, with a Plant Internal Control.Microbes Environ. 2021;36(2):ME21019. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME21019. Microbes Environ. 2021. PMID: 34108359 Free PMC article.
-
Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification for Detection of Plant Pathogens in Wheat (Triticum aestivum).Front Plant Sci. 2022 Mar 15;13:857673. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.857673. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35371152 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LAMP Reaction in Plant Disease Surveillance: Applications, Challenges, and Future Perspectives.Life (Basel). 2024 Nov 26;14(12):1549. doi: 10.3390/life14121549. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768257 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for the detection of Cryptotermes brevis West Indian drywood termite (Blattodea: Kalotermitidae).Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 6;12(1):15111. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-18582-1. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36068251 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid real-time quantitative colorimetric LAMP methodology for field detection of Verticillium dahliae in crude olive-plant samples.Plant Methods. 2024 Sep 9;20(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s13007-024-01251-x. Plant Methods. 2024. PMID: 39252004 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in point-of-care nucleic acid extraction technologies for rapid diagnosis of human and plant diseases.Biosens Bioelectron. 2020 Dec 1;169:112592. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112592. Epub 2020 Sep 8. Biosens Bioelectron. 2020. PMID: 32942143 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid Detection of Pityophthorus juglandis (Blackman) (Coleoptera, Curculionidae) with the Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP) Method.Plants (Basel). 2021 May 22;10(6):1048. doi: 10.3390/plants10061048. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34067342 Free PMC article.
-
A LAMP at the end of the tunnel: A rapid, field deployable assay for the kauri dieback pathogen, Phytophthora agathidicida.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 24;15(1):e0224007. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224007. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31978166 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bilodeau GJ, Lévesque CA, De Cock AW, Duchaine C, Brière S, Uribe P, Martin FN, Hamelin RC. Molecular detection of Phytophthora ramorum by real-time polymerase chain reaction using TaqMan, SYBR Green, and molecular beacons. Phytopathology. 2007;97:632–642. doi: 10.1094/PHYTO-97-5-0632. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bühlmann A, Pothier JF, Rezzonico F, Smits TH, Andreou M, Boonham N, Duffy B, Frey EJ. Erwinia amylovora loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) assay for rapid pathogen detection and on-site diagnosis of fire blight. J Microbiol Meth. 2013;92:332–339. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2012.12.017. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

