Heavy Enzymes and the Rational Redesign of Protein Catalysts
- PMID: 31016852
- PMCID: PMC6900096
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.201900134
Heavy Enzymes and the Rational Redesign of Protein Catalysts
Abstract
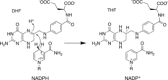
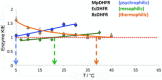
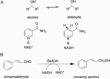
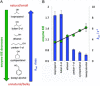
An unsolved mystery in biology concerns the link between enzyme catalysis and protein motions. Comparison between isotopically labelled "heavy" dihydrofolate reductases and their natural-abundance counterparts has suggested that the coupling of protein motions to the chemistry of the catalysed reaction is minimised in the case of hydride transfer. In alcohol dehydrogenases, unnatural, bulky substrates that induce additional electrostatic rearrangements of the active site enhance coupled motions. This finding could provide a new route to engineering enzymes with altered substrate specificity, because amino acid residues responsible for dynamic coupling with a given substrate present as hotspots for mutagenesis. Detailed understanding of the biophysics of enzyme catalysis based on insights gained from analysis of "heavy" enzymes might eventually allow routine engineering of enzymes to catalyse reactions of choice.
Keywords: alcohol dehydrogenases; dihydrofolate reductases; enzyme engineering; isotope effects; molecular dynamics.
© 2019 The Authors. Published by Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bugg T., in Introduction to Enzyme and Coenzyme Chemistry: Second Edition, Blackwell Publishing, Ltd., Oxford, UK, 2004, p. 8.
-
- Tarczykowska A., Kochański B., Kałużny K., Zukow W., J. Educ. Health Sport 2017, 7(9), 217–223.
-
- None
-
- Zhang R., Xu Y., Xiao R., Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1671–1684; - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/J005266/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BB/L020394/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- CTQ2015-66223-C2/Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad/International
- CTQ2015-74523-JIN/Ministerio de Economía, Industria y Competitividad, Gobierno de España/International
- UJI·B2017-31/Universitat Jaume I/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

