LPS‑induced upregulation of the TLR4 signaling pathway inhibits osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells under inflammatory conditions
- PMID: 31017254
- PMCID: PMC6488177
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2019.4165
LPS‑induced upregulation of the TLR4 signaling pathway inhibits osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells under inflammatory conditions
Abstract
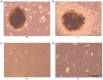
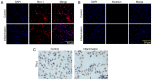
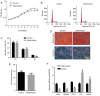
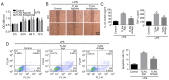
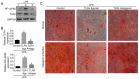
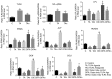
Toll‑like receptor 4 (TLR4) is a transmembrane receptor responsible for the activation of a number of signal transduction pathways. Despite its involvement in inflammatory processes, the regulation of TLR4 signaling in human periodontal ligament stem cells (hPDLSCs) under inflammatory conditions remains to be fully elucidated. The present study aimed to clarify the regulatory mechanisms of the TLR4 signaling pathway and its role in the differentiation of hPDLSCs under inflammatory conditions. hPDLSCs from the periodontal tissues of healthy subjects and patients with periodontitis were identified by analyzing their cell surface marker molecules, and their osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation abilities. To determine the effect of TLR4 signaling on osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation under inflammatory conditions, cells were challenged with TLR4 agonist and antagonist under pluripotent differentiation conditions. Cell proliferation, apoptosis and migration were then determined using appropriate methods. The alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity, Alizarin Red staining, Oil red O staining and relative gene and protein levels expression were also determined. The results showed that lipopolysaccharide (LPS)‑induced inflammation inhibited cell proliferation and migration, promoted cell apoptosis and affected the cell cycle. Under inflammatory conditions, the activation of TLR4 decreased the activity of ALP and the expression of osteogenic markers, including osteocalcin, Runt‑related transcription factor 2 and collagen I, compared with the control group, but increased the expression of adipogenesis‑related genes poly (ADP‑ribose) polymerase γ and lipoprotein lipase. The activation of TLR4 also induced the expression of proinflammatory cytokines interleukin‑1β, tumor necrosis factor‑α, nuclear factor‑κBP65 and TLR4, compared with that in the control group and the TLR4 antagonist group. The findings showed that LPS‑induced upregulation of the TLR4 signaling pathway inhibited osteogenic differentiation and induced adipogenesis of the hPDLSCs under inflammatory conditions. The present study provided a novel understanding of the physiopathology of periodontitis, and a novel avenue for targeted treatments based on stem cell regeneration.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lipopolysaccharide inhibits osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells partially through toll-like receptor 4-mediated ephrinB2 downregulation.Clin Oral Investig. 2020 Oct;24(10):3407-3416. doi: 10.1007/s00784-020-03211-w. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Clin Oral Investig. 2020. PMID: 31974644
-
Effects of sitagliptin activation of the stromal cell-derived factor-1/CXC chemokine receptor 4 signaling pathway on the proliferation, apoptosis, inflammation, and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells induced by lipopolysaccharide.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024 Feb 1;42(1):37-45. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2024.2023213. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38475949 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Salvianolic Acid C Attenuates LPS-Induced Inflammation and Apoptosis in Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells via Toll-Like Receptors 4 (TLR4)/Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-κB) Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Dec 13;25:9499-9508. doi: 10.12659/MSM.918940. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31831723 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Mechanical Force Stress on the Inflammatory Response in Human Periodontal Ligament Cells.Int Dent J. 2025 Feb;75(1):117-126. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2024.12.001. Epub 2024 Dec 26. Int Dent J. 2025. PMID: 39730290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The signaling pathways involved in non-coding RNA regulation during osteogenic differentiation of periodontal tissue-derived cells in the field of periodontitis.J Periodontal Res. 2024 Feb;59(1):18-31. doi: 10.1111/jre.13199. Epub 2023 Nov 14. J Periodontal Res. 2024. PMID: 37961979 Review.
Cited by
-
Endosomal TLR3 signaling in stromal osteoblasts induces prostaglandin E2-mediated inflammatory periodontal bone resorption.J Biol Chem. 2022 Mar;298(3):101603. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101603. Epub 2022 Jan 29. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35101442 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA potassium voltage-gated channel subfamily Q member 1 overlapping transcript 1 regulates the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells by targeting miR-24-3p.Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Oct 1;39(5):547-554. doi: 10.7518/hxkq.2021.05.008. Hua Xi Kou Qiang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34636202 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Understanding the role of iron/heme metabolism in the anti‑inflammatory effects of natural sulfur molecules against lipopolysaccharide‑induced inflammation.Mol Med Rep. 2025 Jul;32(1):177. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13542. Epub 2025 Apr 25. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40280116 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing FOXA1 suppresses inflammation caused by LPS and promotes osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells through the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway.Biomol Biomed. 2025 Apr 3;25(5):1138-1149. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.11367. Biomol Biomed. 2025. PMID: 39760528 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Pulmonoprotective Effect of Natural Prolyl Oligopeptidase Inhibitors in In Vitro and In Vivo Models of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 18;24(18):14235. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814235. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kulkarni V, Bhatavadekar NB, Uttamani JR. The effect of nutrition on periodontal disease: A systematic review. J Calif Dent Assoc. 2014;42:302–311. - PubMed

