Hydrogen sulfide inhibits calcification of heart valves; implications for calcific aortic valve disease
- PMID: 31017307
- PMCID: PMC7024713
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14691
Hydrogen sulfide inhibits calcification of heart valves; implications for calcific aortic valve disease
Abstract
Background and purpose: Calcification of heart valves is a frequent pathological finding in chronic kidney disease and in elderly patients. Hydrogen sulfide (H2 S) may exert anti-calcific actions. Here we investigated H2 S as an inhibitor of valvular calcification and to identify its targets in the pathogenesis.
Experimental approach: Effects of H2 S on osteoblastic transdifferentiation of valvular interstitial cells (VIC) isolated from samples of human aortic valves were studied using immunohistochemistry and western blots. We also assessed H2S on valvular calcification in apolipoprotein E-deficient (ApoE-/- ) mice.
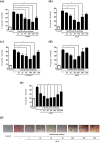
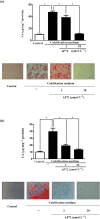
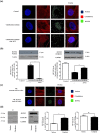
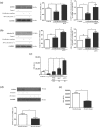
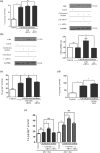
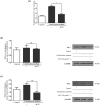
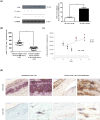
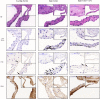
Key results: In human VIC, H2 S from donor compounds (NaSH, Na2 S, GYY4137, AP67, and AP72) inhibited mineralization/osteoblastic transdifferentiation, dose-dependently in response to phosphate. Accumulation of calcium in the extracellular matrix and expression of osteocalcin and alkaline phosphatase was also inhibited. RUNX2 was not translocated to the nucleus and phosphate uptake was decreased. Pyrophosphate generation was increased via up-regulating ENPP2 and ANK1. Lowering endogenous production of H2 S by concomitant silencing of cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE) and cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) favoured VIC calcification. analysis of human specimens revealed higher Expression of CSE in aorta stenosis valves with calcification (AS) was higher than in valves of aortic insufficiency (AI). In contrast, tissue H2 S generation was lower in AS valves compared to AI valves. Valvular calcification in ApoE-/- mice on a high-fat diet was inhibited by H2 S.
Conclusions and implications: The endogenous CSE-CBS/H2 S system exerts anti-calcification effects in heart valves providing a novel therapeutic approach to prevent hardening of valves.
Linked articles: This article is part of a themed section on Hydrogen Sulfide in Biology & Medicine. To view the other articles in this section visit http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/bph.v177.4/issuetoc.
© 2019 The Authors. British Journal of Pharmacology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. M.W. has patent applications for the therapeutic use of slow‐release hydrogen sulfide donor molecules.
Figures
References
-
- Adeney, K. L. , Siscovick, D. S. , Ix, J. H. , Seliger, S. L. , Shlipak, M. G. , Jenny, N. S. , & Kestenbaum, B. R. (2009). Association of serum phosphate with vascular and valvular calcification in moderate CKD. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, 20(2), 381–387. 10.1681/asn.2008040349 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ang, A. D. , Konigstorfer, A. , Giles, G. I. , & Bhatia, M. (2012). Measuring free tissue sulfide. Advances in Biological Chemistry, 02(04), 6 10.4236/abc.2012.24044 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

