The Austrian UVA-Network
- PMID: 31017671
- PMCID: PMC6852124
- DOI: 10.1111/php.13111
The Austrian UVA-Network
Abstract
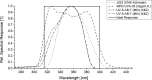
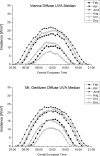
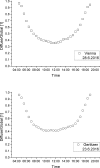
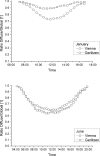
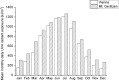
The ultraviolet-A (UVA) part of the solar spectrum at the Earth's surface is an essential environmental factor but continuous long-time monitoring of UVA radiation is rarely done. In Austria, three existing stations of the UV monitoring network have been upgraded with UVA broadband instruments. At each station, one instrument measures global UVA irradiance and-in parallel-a second instrument measures diffuse irradiance. Recent and past measurements are available via a web page. This paper describes the used instruments, calibration and quality assurance and control procedures. Global and diffuse UVA measurements during a period of up to 5 years are presented. Data indicate clear annual courses and an increase of UVA with altitude by 8-9% per 1000 m. In the first half of the year, UVA radiation is higher than in the second half, due to less cloudiness. In Vienna (153 m asl), the mean daily global UVA radiant exposure in summer is almost as high as at Mt. Gerlitzen (1540 m asl), equalizing the altitude effect, due to less cloudiness. However, in winter, the UVA radiant exposure at Mt. Gerlitzen is double as high, as in Vienna.
© 2019 The Authors. Photochemistry and Photobiology published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Society for Photobiology.
Figures




References
-
- Gröbner, J. (2001) Characterisation of spectrophotometers used for spectral solar ultraviolet radiation measurements. Radiat. Prot. Dosim. 97, 415–418. - PubMed
-
- WMO/GAW (2010) Instruments to Measure Solar Ultraviolet Radiation Part 3: Multi‐channel Filter Instruments. GAW. Report no. 190, WMO/TD‐No. 1537, WMO, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- Schmalwieser, A.W. , Gröbner J., Blumthaler M., Klotz B., De Backer H., Bolsée D., Werner R., Tomsic D., Metelka L., Eriksen P., Jepsen N., Aun M., Heikkilä A., Duprat T., Sandmann H., Weiss T., Bais A., Toth Z., Siani A.M., Vaccaro L., Diémoz H., Grifoni D., Zipoli G., Lorenzetto G., Petkov B.H., di Sarra A.G., Massen F., Yousif C., Aculinin A.A., den Outer P., Svendby T., Dahlback A., Johnsen B., Biszczuk‐Jakubowska J., Krzyscin J., Henriques D., Chubarova N., Kolarž P., Mijatovic Z., Groselj D., Pribullova A., Gonzales J.R.M., Bilbao J., Guerrero J.M.V., Serrano A., Andersson S., Vuilleumier L., Webb A. and O'Hagan J. (2017) UV Index monitoring in Europe. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 16, 1349–1370. - PubMed
-
- Lubbock, Sir J. (1881) Observations on ants, bees, and wasps. VIII. Experiments with light of different wave‐lengths. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. 15, 362–387.
-
- Lubbock, Sir J. (1882) On the sense of color among some of the lower animals. J. Linn. Soc. Lond. 16, 121–127.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

