Sustained Ca2+ mobilizations: A quantitative approach to predict their importance in cell-cell communication and wound healing
- PMID: 31017899
- PMCID: PMC6481807
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0213422
Sustained Ca2+ mobilizations: A quantitative approach to predict their importance in cell-cell communication and wound healing
Abstract
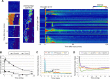
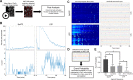
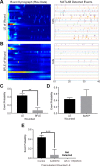
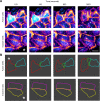
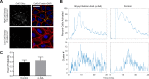
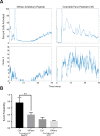
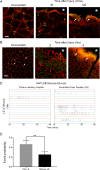
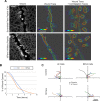
Epithelial wound healing requires the coordination of cells to migrate as a unit over the basement membrane after injury. To understand the process of this coordinated movement, it is critical to study the dynamics of cell-cell communication. We developed a method to characterize the injury-induced sustained Ca2+ mobilizations that travel between cells for periods of time up to several hours. These events of communication are concentrated along the wound edge and are reduced in cells further away from the wound. Our goal was to delineate the role and contribution of these sustained mobilizations and using MATLAB analyses, we determined the probability of cell-cell communication events in both in vitro models and ex vivo organ culture models. We demonstrated that the injury response was complex and represented the activation of a number of receptors. In addition, we found that pannexin channels mediated the cell-cell communication and motility. Furthermore, the sustained Ca2+ mobilizations are associated with changes in cell morphology and motility during wound healing. The results demonstrate that both purinoreceptors and pannexins regulate the sustained Ca2+ mobilization necessary for cell-cell communication in wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

References
-
- Klepeis VE, Cornell-Bell A, Trinkaus-Randall V. Growth factors but not gap junctions play a role in injury-induced Ca2+ waves in epithelial cells. Journal of Cell Science. 2001. December 1;114(23):4185–95. - PubMed
-
- Lu W, Hu H, Sévigny J, Gabelt BT, Kaufman PL, Johnson EC, et al. Rat, mouse, and primate models of chronic glaucoma show sustained elevation of extracellular atp and altered purinergic signaling in the posterior eye. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2015. May 1;56(5):3075–83. 10.1167/iovs.14-15891 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

