Heterozygosity mapping for human dominant trait variants
- PMID: 31018026
- PMCID: PMC6617796
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.23765
Heterozygosity mapping for human dominant trait variants
Abstract
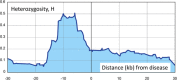
Homozygosity mapping is a well-known technique to identify runs of homozygous variants that are likely to harbor genes responsible for autosomal recessive disease, but a comparable method for autosomal dominant traits has been lacking. We developed an approach to map dominant disease genes based on heterozygosity frequencies of sequence variants in the immediate vicinity of a dominant trait. We demonstrate through theoretical analysis that DNA variants surrounding an inherited dominant disease variant tend to have increased heterozygosity compared with variants elsewhere in the genome. We confirm existence of this phenomenon in sequence data with known dominant pathogenic variants obtained on family members and in unrelated population controls. A computer-based approach to estimating empirical significance levels associated with our test statistics shows genome-wide p-values smaller than 0.05 for many but not all of the individuals carrying a pathogenic variant.
Keywords: ALSPAC; computer simulation; gene mapping; genetic association analysis; sequence variants.
© 2019 The Authors. Human Mutation Published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ataei‐Kachouei, M. , Nadaf, J. , Akbari, M. T. , Atri, M. , Majewski, J. , Riazalhosseini, Y. , & Garshasbi, M. (2015). Double heterozygosity of BRCA2 and STK11 in familial breast cancer detected by exome sequencing. Iranian Journal of Public Health, 44(10), 1348–1352. Retrieved from. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26576347 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bespalova, I. N. , Van Camp, G. , Bom, S. J. , Brown, D. J. , Cryns, K. , DeWan, A. T. , … Lesperance, M. M. (2001). Mutations in the Wolfram syndrome 1 gene (WFS1) are a common cause of low frequency sensorineural hearing loss. Human Molecular Genetics, 10(22), 2501–2508. Retrieved from. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11709537 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boyd, A. , Golding, J. , Macleod, J. , Lawlor, D. A. , Fraser, A. , Henderson, J. , & Davey Smith, G. (2013). Cohort Profile: The ‘children of the 90s’—the index offspring of the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children. International Journal of Epidemiology, 42(1), 111–127. 10.1093/ije/dys064 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Feder, J. N. , Gnirke, A. , Thomas, W. , Tsuchihashi, Z. , Ruddy, D. A. , Basava, A. , … Wolff, R. K. (1996). A novel MHC class I‐like gene is mutated in patients with hereditary haemochromatosis. Nature Genetics, 13(4), 399–408. Retrieved from. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?cmd=Retrieve&db=PubMed&dop... - PubMed
-
- Fraser, A. , Macdonald‐Wallis, C. , Tilling, K. , Boyd, A. , Golding, J. , Davey Smith, G. , … Lawlor, D. A. (2013). Cohort Profile: The Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children: ALSPAC mothers cohort. International Journal of Epidemiology, 42(1), 97–110. 10.1093/ije/dys066 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- U54 HG006493/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC003594/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG008972/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG006493/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- G9815508/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- DC011651/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_19009/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R29 DC003594/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC011651/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- DC003594/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG058131/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

