Autophagy in Pulmonary Innate Immunity
- PMID: 31018206
- PMCID: PMC6959120
- DOI: 10.1159/000497414
Autophagy in Pulmonary Innate Immunity
Abstract
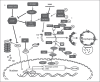
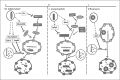
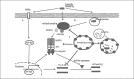
Autophagy is a major intracellular digestion system that delivers cytoplasmic components for degradation and recycling. In this capacity, autophagy plays an important role in maintaining cellular homeostasis by mediating the degradation of cellular macromolecules and dysfunctional organelles and regeneration of nutrients for cell growth. Autophagy is important in innate immunity, as it is responsible for the clearance of various pathogens. Deficiency of intracellular autophagy can result in exaggerated activation of the inflammasome. The latter is an innate immune complex that senses diverse pathogen-associated or danger-associated molecular patterns and activates the expression of inflammatory cytokines. In autophagy-deficient cells, accumulation of damaged organelles, misfolded proteins, and reactive oxygen species contribute to inflammasome activation. The lung is continuously exposed to pathogens from the environment, rendering it vulnerable to infection. The lung innate immune cells act as a crucial initial barrier against the continuous threat from pathogens. In this review, we will summarize recent findings on the regulation of autophagy and its inter-action with innate immunity, focusing on the lung.
Keywords: Autophagy; Inflammasome; Innate immunity and pulmonary inflammation; Pathogen.
© 2019 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Mizushima N, Komatsu M. Autophagy: renovation of cells and tissues. Cell. 2011 Nov;147((4)):728–41. - PubMed
-
- Gutierrez MG, Master SS, Singh SB, Taylor GA, Colombo MI, Deretic V. Autophagy is a defense mechanism inhibiting BCG and Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival in infected macrophages. Cell. 2004 Dec;119((6)):753–66. - PubMed
-
- Jagannath C, Lindsey DR, Dhandayuthapani S, Xu Y, Hunter RL, Jr, Eissa NT. Autophagy enhances the efficacy of BCG vaccine by increasing peptide presentation in mouse dendritic cells. Nat Med. 2009 Mar;15((3)):267–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

