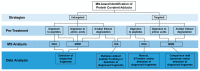
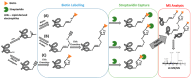
Mass Spectrometry-Based Methodologies for Targeted and Untargeted Identification of Protein Covalent Adducts (Adductomics): Current Status and Challenges
- PMID: 31018479
- PMCID: PMC6631461
- DOI: 10.3390/ht8020009
Mass Spectrometry-Based Methodologies for Targeted and Untargeted Identification of Protein Covalent Adducts (Adductomics): Current Status and Challenges
Abstract
Protein covalent adducts formed upon exposure to reactive (mainly electrophilic) chemicals may lead to the development of a wide range of deleterious health outcomes. Therefore, the identification of protein covalent adducts constitutes a huge opportunity for a better understanding of events underlying diseases and for the development of biomarkers which may constitute effective tools for disease diagnosis/prognosis, for the application of personalized medicine approaches and for accurately assessing human exposure to chemical toxicants. The currently available mass spectrometry (MS)-based methodologies, are clearly the most suitable for the analysis of protein covalent modifications, providing accuracy, sensitivity, unbiased identification of the modified residue and conjugates along with quantitative information. However, despite the huge technological advances in MS instrumentation and bioinformatics tools, the identification of low abundant protein covalent adducts is still challenging. This review is aimed at summarizing the MS-based methodologies currently used for the identification of protein covalent adducts and the strategies developed to overcome the analytical challenges, involving not only sample pre-treatment procedures but also distinct MS and data analysis approaches.
Keywords: adductomics; mass spectrometry; protein covalent adducts.
Conflict of interest statement
SRM, selected reaction monitoring
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Metabolomics-Inspired Strategy for the Identification of Protein Covalent Modifications.Front Chem. 2019 Jul 31;7:532. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00532. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2019. PMID: 31417895 Free PMC article.
-
16α-Hydroxyestrone: Mass Spectrometry-Based Methodologies for the Identification of Covalent Adducts Formed with Blood Proteins.Chem Res Toxicol. 2020 Aug 17;33(8):2147-2156. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.0c00171. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Chem Res Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32692160
-
Adductomics: a promising tool for the verification of chemical warfare agents' exposures in biological samples.Arch Toxicol. 2019 Jun;93(6):1473-1484. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02435-4. Epub 2019 Mar 28. Arch Toxicol. 2019. PMID: 30923868 Review.
-
Emerging Technologies in Mass Spectrometry-Based DNA Adductomics.High Throughput. 2019 May 14;8(2):13. doi: 10.3390/ht8020013. High Throughput. 2019. PMID: 31091740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of an untargeted DNA adductomics method by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry.Talanta. 2025 Jan 1;282:126985. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2024.126985. Epub 2024 Oct 5. Talanta. 2025. PMID: 39418978
Cited by
-
Multi-adductomics: Advancing mass spectrometry techniques for comprehensive exposome characterization.Trends Analyt Chem. 2024 Nov;180:117900. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2024.117900. Epub 2024 Aug 5. Trends Analyt Chem. 2024. PMID: 39246549
-
The mercapturomic profile of health and non-communicable diseases.High Throughput. 2019 Apr 23;8(2):10. doi: 10.3390/ht8020010. High Throughput. 2019. PMID: 31018482 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Covalent Histone Modification by an Electrophilic Derivative of the Anti-HIV Drug Nevirapine.Molecules. 2021 Mar 3;26(5):1349. doi: 10.3390/molecules26051349. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33802579 Free PMC article.
-
Covalent Modification of Proteins by Plant-Derived Natural Products: Proteomic Approaches and Biological Impacts.Proteomics. 2021 Feb;21(3-4):e1900386. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201900386. Epub 2020 Dec 31. Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 32949481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human brains preserve in diverse environments for at least 12 000 years.Proc Biol Sci. 2024 Mar 27;291(2019):20232606. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2023.2606. Epub 2024 Mar 20. Proc Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38503334 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hardt U., Larsson A., Gunnarsson I., Clancy R.M., Petri M., Buyon J.P., Silverman G.J., Svenungsson E., Grönwall C. Autoimmune reactivity to malondialdehyde adducts in systemic lupus erythematosus is associated with disease activity and nephritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2018;20:36. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1530-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources