Identification of the Actinomycin D Biosynthetic Pathway from Marine-Derived Streptomyces costaricanus SCSIO ZS0073
- PMID: 31018504
- PMCID: PMC6521150
- DOI: 10.3390/md17040240
Identification of the Actinomycin D Biosynthetic Pathway from Marine-Derived Streptomyces costaricanus SCSIO ZS0073
Abstract
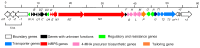
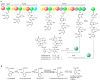
Bioactive secondary metabolites from Streptomycetes are important sources of lead compounds in current drug development. Streptomyces costaricanus SCSIO ZS0073, a mangrove-derived actinomycete, produces actinomycin D, a clinically used therapeutic for Wilm's tumor of the kidney, trophoblastic tumors and rhabdomyosarcoma. In this work, we identified the actinomycin biosynthetic gene cluster (BGC) acn by detailed analyses of the S. costaricanus SCSIO ZS0073 genome. This organism produces actinomycin D with a titer of ~69.8 μg mL-1 along with traces of actinomycin Xoβ. The acn cluster localized to a 39.8 kb length region consisting of 25 open reading frames (ORFs), including a set of four genes that drive the construction of the 4-methyl-3-hydroxy-anthranilic acid (4-MHA) precursor and three non-ribosomal peptide synthetases (NRPSs) that generate the 4-MHA pentapeptide semi-lactone, which, upon dimerization, affords final actinomycin D. Furthermore, the acn cluster contains four positive regulatory genes acnWU4RO, which were identified by in vivo gene inactivation studies. Our data provide insights into the genetic characteristics of this new mangrove-derived actinomycin D bioproducer, enabling future metabolic engineering campaigns to improve both titers and the structural diversities possible for actinomycin D and related analogues.
Keywords: Streptomyces costaricanus; actinomycin D; bioproducer; biosynthesis; biosynthetic gene cluster.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The actinomycin biosynthetic gene cluster of Streptomyces chrysomallus: a genetic hall of mirrors for synthesis of a molecule with mirror symmetry.J Bacteriol. 2010 May;192(10):2583-95. doi: 10.1128/JB.01526-09. Epub 2010 Mar 19. J Bacteriol. 2010. PMID: 20304989 Free PMC article.
-
Mutasynthesis of Antibacterial Halogenated Actinomycin Analogues.J Nat Prod. 2021 Aug 27;84(8):2217-2225. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.1c00294. Epub 2021 Jul 16. J Nat Prod. 2021. PMID: 34270246
-
Acyl pentapeptide lactone synthesis in actinomycin-producing streptomycetes by feeding with structural analogs of 4-methyl-3-hydroxyanthranilic acid.J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8226-31. J Biol Chem. 1984. PMID: 6203903
-
Control of the actinomycin biosynthetic pathway in and actinomycin resistance of Streptomyces spp.J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):598-603. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.598-603.1982. J Bacteriol. 1982. PMID: 6175617 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration and genome mining of natural products from marine Streptomyces.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Jan;104(1):67-76. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-10227-0. Epub 2019 Nov 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31773207 Review.
Cited by
-
A Glossary for Chemical Approaches towards Unlocking the Trove of Metabolic Treasures in Actinomycetes.Molecules. 2021 Dec 27;27(1):142. doi: 10.3390/molecules27010142. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 35011373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biocontrol of strawberry gray mold caused by Botrytis cinerea with the termite associated Streptomyces sp. sdu1201 and actinomycin D.Front Microbiol. 2022 Nov 4;13:1051730. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1051730. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36406410 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Indonesian actinomycete extracts for anti-tubercular compounds: Integrating inhibition assessment, genomic analysis, and prediction of its target by molecular docking.Heliyon. 2024 Aug 4;10(15):e35648. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35648. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170210 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of soil-derived Bacillus subtilis metabolites against breast cancer: In vitro and in silico studies.Saudi Pharm J. 2025 Apr 17;33(1-2):3. doi: 10.1007/s44446-025-00006-6. Saudi Pharm J. 2025. PMID: 40397331 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Vibrio parahaemolyticus compounds from Streptomyces parvus based on Pan-genome and subtractive proteomics.Front Microbiol. 2023 Jul 6;14:1218176. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1218176. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37485508 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hollstein U. Actinomycin. Chemistry and mechanism of action. Chem. Rev. 1974;74:625–652. doi: 10.1021/cr60292a002. - DOI
-
- Cai W.L., Wang X., Elshahawi S.I., Ponomareva L.V., Liu X., McErlean M.R., Cui Z., Arlinghaus A.L., Thorson J.S., Van Lanen S.G. Antibacterial and cytotoxic actinomycins Y6–Y9 and Zp from Streptomyces sp. strain Gö-GS12. J. Nat. Prod. 2016;79:2731–2739. doi: 10.1021/acs.jnatprod.6b00742. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

