Developments in Transduction, Connectivity and AI/Machine Learning for Point-of-Care Testing
- PMID: 31018573
- PMCID: PMC6515310
- DOI: 10.3390/s19081917
Developments in Transduction, Connectivity and AI/Machine Learning for Point-of-Care Testing
Abstract
We review some emerging trends in transduction, connectivity and data analytics for Point-of-Care Testing (POCT) of infectious and non-communicable diseases. The patient need for POCT is described along with developments in portable diagnostics, specifically in respect of Lab-on-chip and microfluidic systems. We describe some novel electrochemical and photonic systems and the use of mobile phones in terms of hardware components and device connectivity for POCT. Developments in data analytics that are applicable for POCT are described with an overview of data structures and recent AI/Machine learning trends. The most important methodologies of machine learning, including deep learning methods, are summarised. The potential value of trends within POCT systems for clinical diagnostics within Lower Middle Income Countries (LMICs) and the Least Developed Countries (LDCs) are highlighted.
Keywords: POCT; artificial intelligence; deep learning; microfluidics; mobile phone; photonics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. This paper does not raise any ethical issues.
Figures

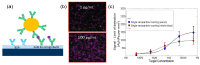
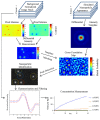

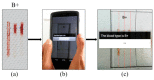


References
-
- Kumar A., Roberts D., Wood K.E., Light B., Parrillo J.E., Sharma S., Suppes R., Feinstein D., Zanotti S., Taiberg L., et al. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit. Care Med. 2006;43:1589–1596. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000217961.75225.E9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Antibiotic/Antimicrobial Resistance (AR/AMR) Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2019.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

