Two Sides of the Coin: Ezrin/Radixin/Moesin and Merlin Control Membrane Structure and Contact Inhibition
- PMID: 31018575
- PMCID: PMC6515277
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20081996
Two Sides of the Coin: Ezrin/Radixin/Moesin and Merlin Control Membrane Structure and Contact Inhibition
Abstract
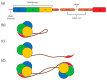
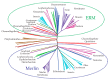
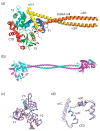
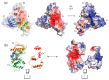
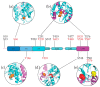
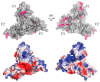
The merlin-ERM (ezrin, radixin, moesin) family of proteins plays a central role in linking the cellular membranes to the cortical actin cytoskeleton. Merlin regulates contact inhibition and is an integral part of cell-cell junctions, while ERM proteins, ezrin, radixin and moesin, assist in the formation and maintenance of specialized plasma membrane structures and membrane vesicle structures. These two protein families share a common evolutionary history, having arisen and separated via gene duplication near the origin of metazoa. During approximately 0.5 billion years of evolution, the merlin and ERM family proteins have maintained both sequence and structural conservation to an extraordinary level. Comparing crystal structures of merlin-ERM proteins and their complexes, a picture emerges of the merlin-ERM proteins acting as switchable interaction hubs, assembling protein complexes on cellular membranes and linking them to the actin cytoskeleton. Given the high level of structural conservation between the merlin and ERM family proteins we speculate that they may function together.
Keywords: FERM domain; ezrin; merlin; moesin; radixin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

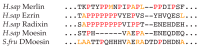


Similar articles
-
CLIC proteins, ezrin, radixin, moesin and the coupling of membranes to the actin cytoskeleton: a smoking gun?Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Feb;1838(2):643-57. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2013.05.025. Epub 2013 Jun 1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 23732235 Review.
-
Interaction between two isoforms of the NF2 tumor suppressor protein, merlin, and between merlin and ezrin, suggests modulation of ERM proteins by merlin.J Neurosci Res. 2000 Nov 15;62(4):491-502. doi: 10.1002/1097-4547(20001115)62:4<491::AID-JNR3>3.0.CO;2-D. J Neurosci Res. 2000. PMID: 11070492
-
Self-masking in an intact ERM-merlin protein: an active role for the central alpha-helical domain.J Mol Biol. 2007 Feb 2;365(5):1446-59. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.10.075. Epub 2006 Oct 26. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17134719 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into a single rod-like helix in activated radixin required for membrane-cytoskeletal cross-linking.Biochemistry. 2003 Oct 14;42(40):11634-41. doi: 10.1021/bi0350497. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 14529273
-
ERM proteins and merlin: integrators at the cell cortex.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002 Aug;3(8):586-99. doi: 10.1038/nrm882. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12154370 Review.
Cited by
-
Hearing loss and vestibular schwannoma: new insights into Schwann cells implication.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Sep 23;14(9):629. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06141-z. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 37741837 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A bipartite NLS motif mediates the nuclear import of Drosophila moesin.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 21;12:1206067. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1206067. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38450250 Free PMC article.
-
Modification of the Mammalian Endomembrane System in Healthy and Diseased Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 20;21(6):2133. doi: 10.3390/ijms21062133. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32244909 Free PMC article.
-
ERM Proteins at the Crossroad of Leukocyte Polarization, Migration and Intercellular Adhesion.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 22;21(4):1502. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041502. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32098334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ezrin Mediates Invasion and Metastasis in Tumorigenesis: A Review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Nov 10;8:588801. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.588801. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33240887 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Turunen O., Sainio M., Jääskeläinen J., Carpén O., Vaheri A. Structure-function relationships in the ezrin family and the effect of tumor-associated point mutations in neurofibromatosis 2 protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 1998;1387:1–16. doi: 10.1016/S0167-4838(98)00103-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

