Limited Knowledge of Chronic Kidney Disease among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in India
- PMID: 31018581
- PMCID: PMC6518175
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph16081443
Limited Knowledge of Chronic Kidney Disease among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients in India
Abstract
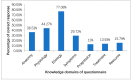
Diabetes and hypertension are the two major causes of chronic kidney disease (CKD). Epidemiological studies have found poor knowledge about the CKD among the general population. Hence, this study aimed to assess the awareness of CKD among type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients in India. Patients with confirmed T2DM were included in the study. Patients receiving dialysis or with a history of a kidney transplant were excluded. A validated questionnaire was used to assess knowledge about CKD. Demographic characteristics were presented using descriptive statistics and trends in groups were calculated using the chi-square test. Statistical analysis was performed using SAS v9.4. A total of 323 patients completed the study. The mean age of the patients was 56 ± 11.25 years, and 51.7% were female. Only 33.43% of the patients correctly identified diabetes and hypertension as risk factors for CKD, while 44.27% were aware of the kidney's function. Statistically significant associations were observed between kidney disease knowledge and education status (p = 0.004), socioeconomic status (p = 0.000), and income status (p = 0.003). No association was observed between the knowledge about CKD and age, gender, hypertension stages, CKD stages, duration of diabetes as well as hypertension and co-morbidities. Based on the results of this study, we found poor knowledge of CKD among Indian T2DM patients. The government should start a CKD awareness programme to deal with this rising co-morbid condition.
Keywords: India; chronic kidney disease; diabetes; diabetic kidney disease; epidemiology; hypertension; public health.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Independent correlates of chronic kidney disease awareness among adults with type 2 diabetes.J Diabetes Complications. 2017 Jun;31(6):988-991. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2017.03.004. Epub 2017 Mar 18. J Diabetes Complications. 2017. PMID: 28363729 Free PMC article.
-
Awareness, knowledge and perception of chronic kidney disease in a rural community of South-West Nigeria.Niger J Clin Pract. 2016 Mar-Apr;19(2):161-9. doi: 10.4103/1119-3077.175960. Niger J Clin Pract. 2016. PMID: 26856275
-
Patient awareness and beliefs about the risk factors and comorbidities associated with chronic kidney disease : A mixed-methods study.Nephrology (Carlton). 2017 May;22(5):374-381. doi: 10.1111/nep.12829. Nephrology (Carlton). 2017. PMID: 27248507
-
Changing epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and associated chronic kidney disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016 Feb;12(2):73-81. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2015.173. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2016. PMID: 26553517 Review.
-
Restorative Dental Treatment in a Patient with Mild to Moderate Chronic Kidney Disease (Stages 1-3).Dent Clin North Am. 2023 Jul;67(3):531-533. doi: 10.1016/j.cden.2023.02.037. Epub 2023 Mar 27. Dent Clin North Am. 2023. PMID: 37244733 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevalence of peripheral neuropathy and associated pain in patients with diabetes mellitus: Evidence from a cross-sectional study.J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020 Jul 31;19(2):1011-1017. doi: 10.1007/s40200-020-00597-y. eCollection 2020 Dec. J Diabetes Metab Disord. 2020. PMID: 33520819 Free PMC article.
-
The proportion of chronic kidney disease and its associated factors among adult diabetic patients at Tibebe Ghion Specialized Hospital, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia.Metabol Open. 2022 Jun 23;15:100198. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2022.100198. eCollection 2022 Sep. Metabol Open. 2022. PMID: 35785137 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of diabetic kidney disease risk using machine learning models: A population-based cohort study of Asian adults.Elife. 2023 Sep 14;12:e81878. doi: 10.7554/eLife.81878. Elife. 2023. PMID: 37706530 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Patient Awareness Regarding Chronic Kidney Disease Management in Santhal Parganas.Indian J Nephrol. 2025 Jan-Feb;35(1):77-81. doi: 10.25259/IJN_14_2024. Epub 2024 Jun 4. Indian J Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 39872270 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge of chronic kidney disease among undergraduate and postgraduate students in a public university in Klang Valley, Malaysia: A cross sectional study.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 23;17(9):e0274038. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274038. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36149873 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levin A., Stevens P.E., Bilous R.W., Coresh J., De Francisco A.L., De Jong P.E., Griffith K.E., Hemmelgarn B.R., Iseki K., Lamb E.J., et al. Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) CKD Work Group. KDIGO 2012 clinical practice guideline for the evaluation and management of chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2013;3:1–150.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical