Lanostane-Type Saponins from Vitaliana primuliflora
- PMID: 31018589
- PMCID: PMC6515439
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24081606
Lanostane-Type Saponins from Vitaliana primuliflora
Abstract
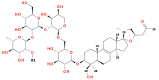
The phytochemistry of the genera Androsace, Cortusa, Soldanella, and Vitaliana, belonging to the Primulaceae family is not well studied so far. Hence, in this paper, we present the results of UHPLC-MS/MS analysis of several primrose family members as well as isolation and structure determination of two new saponins from Vitaliana primuliflora subsp. praetutiana. These two nor-triterpenoid saponins were characterized as (23S)-17α,23-epoxy-29-hydroxy-3β-[(O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-α-l-arabinopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-d-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-27-nor-lanost-8-en-25-one and (23S)-17α,23-epoxy-29-hydroxy-3β-[(O-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-α-l-arabinopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-d-glucopyranosyl)oxy]-27-nor-lanost-8-en-25-one, respectively. Their structures were determined by high resolution mass spectrometry (HRMS), tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS), one- and two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1D-, and 2D-NMR) analyses. So far, the 27-nor-lanostane monodesmosides were rarely found in dicotyledon plants. Therefore their presence in Vitaliana and also in Androsace species belonging to the Aretia section is unique and reported here for the first time. Additionally, eleven other saponins were determined by HRMS and MS/MS spectra. The isolated lanostane saponins can be considered as chemotaxonomic markers of the family Primulaceae.
Keywords: Androsace; Douglasia; Primula; Primulaceae; UHPLC screening; Vitaliana; lanostane; primrose; steroid saponins; triterpenoid saponin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Triterpenoid saponin from Primula elatior subsp. meyeri.J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2001;3(4):347-52. doi: 10.1080/10286020108040375. J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2001. PMID: 11783589
-
Triterpenoid saponins from the roots of Pulsatilla koreana.J Nat Prod. 2005 Feb;68(2):268-72. doi: 10.1021/np049813h. J Nat Prod. 2005. PMID: 15730260
-
Triterpenoid saponins from Lysimachia davurica.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2006 Oct;54(10):1380-3. doi: 10.1248/cpb.54.1380. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2006. PMID: 17015973
-
Triterpenoid saponins from Androsace umbellata and their anti-proliferative activities in human hepatoma cells.Planta Med. 2008 Aug;74(10):1280-4. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1081291. Epub 2008 Jul 11. Planta Med. 2008. PMID: 18622900
-
New triterpenoid saponins from Leontice smirnowii.Fitoterapia. 2010 Oct;81(7):897-901. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2010.05.021. Epub 2010 Jun 8. Fitoterapia. 2010. PMID: 20554004
Cited by
-
Biochemical and Molecular Investigation of the Effect of Saponins and Terpenoids Derived from Leaves of Ilex aquifolium on Lipid Metabolism of Obese Zucker Rats.Molecules. 2022 May 24;27(11):3376. doi: 10.3390/molecules27113376. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35684317 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Ilex × meserveae S. Y. Hu Extract and Its Fractions on Renal Morphology in Rats Fed with Normal and High-Cholesterol Diet.Foods. 2021 Apr 9;10(4):818. doi: 10.3390/foods10040818. Foods. 2021. PMID: 33918905 Free PMC article.
-
In Search of High-Yielding and Single-Compound-Yielding Plants: New Sources of Pharmaceutically Important Saponins from the Primulaceae Family.Biomolecules. 2020 Feb 29;10(3):376. doi: 10.3390/biom10030376. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32121337 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials