Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Underlying Casein Allergy Is Suppressed by Extracellular Vesicles Carrying miRNA-150
- PMID: 31018604
- PMCID: PMC6521277
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11040907
Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity Underlying Casein Allergy Is Suppressed by Extracellular Vesicles Carrying miRNA-150
Abstract
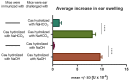
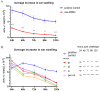
In patients with non-IgE-mediated milk allergy, a cellular mechanism of delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) is considered. Recent findings prove that cell-mediated reactions can be antigen-specifically inhibited by extracellular vesicles (EVs) carrying miRNA-150. We sought to establish a new mouse model of DTH to casein and test the possibility of antigen-specific suppression of the inflammatory reaction. To produce soluble antigenic peptides, casein was subjected to alkaline hydrolysis. DTH reaction to casein was induced in CBA, C57BL/6, and BALB/c mice by intradermal (id) injection of the antigen. Cells collected from spleens and lymph nodes were positively or negatively selected and transferred to naive recipients intravenously (iv). CBA mice were tolerized by iv injection of mouse erythrocytes conjugated with casein antigen and following id immunization with the same antigen. Suppressive EVs were harvested from cell cultures and serum of tolerized donors by means of ultrafiltration and ultracentrifugation for further therapeutic utilization. The newly established mouse model of DTH to casein was mediated by CD4+ Th1 cells and macrophages, while EVs produced by casein-tolerized animals effectively suppressed effector cell response, in an miRNA-150-dependent manner. Altogether, our observations contribute to the current understanding of non-IgE-mediated allergy to casein and of the possibilities to downregulate this reaction.
Keywords: casein; cell-mediated reactions; cow’s milk allergy; delayed-type hypersensitivity; extracellular vesicles; miRNA-150.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Orally Administered Exosomes Suppress Mouse Delayed-Type Hypersensitivity by Delivering miRNA-150 to Antigen-Primed Macrophage APC Targeted by Exosome-Surface Anti-Peptide Antibody Light Chains.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 2;21(15):5540. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155540. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32748889 Free PMC article.
-
Syngeneic red blood cell-induced extracellular vesicles suppress delayed-type hypersensitivity to self-antigens in mice.Clin Exp Allergy. 2019 Nov;49(11):1487-1499. doi: 10.1111/cea.13475. Epub 2019 Aug 26. Clin Exp Allergy. 2019. PMID: 31365154 Free PMC article.
-
Delayed-type hypersensitivity initiation by early-acting cells that are antigen mismatched or MHC incompatible with late-acting, delayed-type hypersensitivity effector T cells.J Immunol. 1991 Jan 15;146(2):469-75. J Immunol. 1991. PMID: 1987274
-
T cell responses induced by the parenteral injection of antigen-modified syngeneic cells. I. Induction, characterization, and regulation of antigen-specific T helper cells involved in delayed-type hypersensitivity responses.J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):77-85. J Immunol. 1983. PMID: 6190929
-
Regulation of delayed type hypersensitivity to host histocompatibility antigens during graft-versus-host reactions.Immunol Rev. 1985 Dec;88:25-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1985.tb01152.x. Immunol Rev. 1985. PMID: 2935486 Review.
Cited by
-
mTOR Signaling in Macrophages: All Depends on the Context.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 6;26(15):7598. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157598. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806725 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exosome as a Delivery Vehicle for Cancer Therapy.Cells. 2022 Jan 18;11(3):316. doi: 10.3390/cells11030316. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Increasing the Therapeutic Efficacy of Extracellular Vesicles From the Antigen-Specific Antibody and Light Chain Perspective.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Nov 24;9:790722. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.790722. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34901032 Free PMC article.
-
Ancient Evolutionary Origin and Properties of Universally Produced Natural Exosomes Contribute to Their Therapeutic Superiority Compared to Artificial Nanoparticles.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 31;22(3):1429. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031429. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33572657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
COVID-19 therapy with mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) and convalescent plasma must consider exosome involvement: Do the exosomes in convalescent plasma antagonize the weak immune antibodies?J Extracell Vesicles. 2020 Oct;10(1):e12004. doi: 10.1002/jev2.12004. Epub 2020 Nov 14. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020. PMID: 33304473 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wąsik M., Nazimek K., Bryniarski K. Allergic reactions to cow’s milk: Pathomechanism, diagnostic and therapeutic strategies, possibilities of food tolerance induction. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2018;72:1–11. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0011.8254. (In Polish) - DOI
-
- Díaz M., Guadamuro L., Espinosa-Martos I., Mancabelli L., Jiménez S., Molinos-Norniella C., Pérez-Solis D., Milani C., Rodríguez J.M., Ventura M., et al. Microbiota and Derived Parameters in Fecal Samples of Infants with Non-IgE Cow’s Milk Protein Allergy under a Restricted Diet. Nutrients. 2018;10:1481. doi: 10.3390/nu10101481. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

