Cytotoxic Withanolides from the Whole Herb of Physalis angulata L
- PMID: 31018606
- PMCID: PMC6514790
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24081608
Cytotoxic Withanolides from the Whole Herb of Physalis angulata L
Abstract
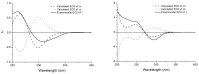
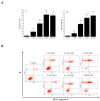
Physalis angulata L. is a medicinal plant of the Solanaceae family, which is used to produce a variety of steroids. The present study reports on the cytotoxic withanolides of this plant. The species of Physalis angulata L. was identified by DNA barcoding techniques. Two new withanolides (1-2), together with six known analogues (3-8), were isolated from the whole plant of Physalis angulata L. The structures of these new compounds were determined on the basis of extensive spectroscopic data analyses and electronic circular dichroism (ECD) calculations. The withanolides exhibited strong cytotoxic activities against A549, Hela and p388 cell lines. Furthermore, compounds 1 and 2 induced typical apoptotic cell death in A549 cell line according to the evaluation of the apoptosis-inducing activity by flow cytometric analysis.
Keywords: Physalis angulata L.; Solanaceae; cytotoxic activities; withanolides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Isolation and characterization of cytotoxic withanolides from the calyx of Physalis alkekengi L. var franchetii.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Mar;96:103614. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103614. Epub 2020 Jan 25. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 32007725
-
Cytotoxic withanolides from Physalis angulata.Nat Prod Res. 2018 Mar;32(6):676-681. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2017.1338281. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Nat Prod Res. 2018. PMID: 28617049
-
Target discovery of cytotoxic withanolides from Physalis angulata var. villosa via reactivity-based screening.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Mar 20;151:194-199. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.12.047. Epub 2018 Jan 9. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018. PMID: 29367159
-
Withanolides from the genus Physalis: a review on their phytochemical and pharmacological aspects.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2020 May;72(5):649-669. doi: 10.1111/jphp.13209. Epub 2019 Dec 11. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31826333 Review.
-
Antiproliferative withanolides from several solanaceous species.Nat Prod Res. 2014;28(22):1941-51. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2014.919286. Epub 2014 May 28. Nat Prod Res. 2014. PMID: 24871278 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hidden in Plants-A Review of the Anticancer Potential of the Solanaceae Family in In Vitro and In Vivo Studies.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Mar 11;14(6):1455. doi: 10.3390/cancers14061455. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35326606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fascinating Furanosteroids and Their Pharmacological Profile.Molecules. 2023 Jul 26;28(15):5669. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155669. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37570639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical Composition Analysis, Cytotoxic, Antimicrobial and Antioxidant Activities of Physalis angulata L.: A Comparative Study of Leaves and Fruit.Molecules. 2022 Feb 22;27(5):1480. doi: 10.3390/molecules27051480. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35268579 Free PMC article.
-
Untargeted Chemical Profile, Antioxidant, and Enzyme Inhibition Activity of Physalis angulata L. from the Peruvian Amazon: A Contribution to the Validation of Its Pharmacological Potential.Antioxidants (Basel). 2025 Feb 20;14(3):246. doi: 10.3390/antiox14030246. Antioxidants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40227212 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Chemistry and Therapeutic Evaluation of Naturally Occurring and Synthetic Withanolides.Molecules. 2022 Jan 28;27(3):886. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030886. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35164150 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Yang Y.J., Chen M.G., Hu L., Zhu D.N. Chemical Constituents of Whole Plant of Physalis angulata L. Chin. Pharm. J. 2013;48:1715–1718.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

