Regulation of dendritic cell function improves survival in experimental sepsis through immune chaperone
- PMID: 31018807
- PMCID: PMC6830886
- DOI: 10.1177/1753425919840423
Regulation of dendritic cell function improves survival in experimental sepsis through immune chaperone
Abstract
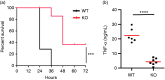
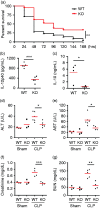
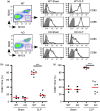
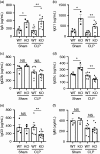
Dendritic cells (DCs) are professional Ag-presenting cells that play a critical role in both innate and adaptive immune responses. DCs recognize and respond to bacteria through multiple PRRs, including TLRs. Heat shock protein gp96/grp94 is a master essential chaperone for TLRs in the endoplasmic reticulum. We generated DC-specific gp96-knockout (KO) mice and showed that gp96 KO DCs were unable to respond to multiple TLR ligands. TLR-mediated hyperinflammatory response can lead to sepsis. However, the roles of neither DCs nor the DC-intrinsic gp96 in the process are completely understood. In a LPS-induced sepsis model, we hereby found that deletion of gp96 in DCs significantly reduced serum TNF-α levels and improved survival. Furthermore, using the well-defined polymicrobial sepsis model of cecal ligation and puncture, we found that DC-specific ablation of gp96 improved survival with significantly attenuated liver and renal injuries, decreased circulating inflammatory cytokines, altered DC maturation and activation, and increased serum Ig. Collectively, we demonstrate that deletion of gp96 in DCs is beneficial in protecting mice against sepsis induced by both endotoxemia and polymicrobial infections. We conclude that targeting gp96 in DCs may provide a potential novel approach for reducing the morbidity and mortality of sepsis.
Keywords: Dendritic cell; TLR; chaperone; gp96/grp94; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glucose-regulated protein 94/glycoprotein 96 elicits bystander activation of CD4+ T cell Th1 cytokine production in vivo.J Immunol. 2004 Apr 1;172(7):4195-203. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.7.4195. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15034032
-
Cross-presentation of glycoprotein 96-associated antigens on major histocompatibility complex class I molecules requires receptor-mediated endocytosis.J Exp Med. 2000 Jun 5;191(11):1965-74. doi: 10.1084/jem.191.11.1965. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 10839811 Free PMC article.
-
Cell surface targeting of heat shock protein gp96 induces dendritic cell maturation and antitumor immunity.J Immunol. 2001 Dec 15;167(12):6731-5. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.12.6731. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11739487
-
The heat shock protein gp96: a receptor-targeted cross-priming carrier and activator of dendritic cells.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2000 Nov;5(5):462-70. doi: 10.1379/1466-1268(2000)005<0462:thspga>2.0.co;2. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2000. PMID: 11189453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dendritic cells from bench to bedside and back.Immunol Lett. 2009 Feb 21;122(2):128-30. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2008.11.017. Epub 2008 Dec 31. Immunol Lett. 2009. PMID: 19121337 Review.
Cited by
-
Dysregulated dendritic cells in sepsis: functional impairment and regulated cell death.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024 May 30;29(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s11658-024-00602-9. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2024. PMID: 38816685 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The development of endoplasmic reticulum-related gene signatures and the immune infiltration analysis of sepsis.Front Immunol. 2023 Jun 6;14:1183769. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1183769. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37346041 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of Genetic Variants in HSP90 Genes-Complex in COPD Secondary to Biomass-Burning Smoke Exposure and Non-Severe COPD Forms in Tobacco Smoking Subjects.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2021 Aug 3;43(2):887-899. doi: 10.3390/cimb43020063. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34449539 Free PMC article.
-
Disparate Recruitment and Retention of Plasmacytoid Dendritic Cells to The Small Intestinal Mucosa between Young and Aged Mice.Aging Dis. 2021 Aug 1;12(5):1183-1196. doi: 10.14336/AD.2021.0119. eCollection 2021 Aug. Aging Dis. 2021. PMID: 34341701 Free PMC article.
-
TNF-α-induced protein 8-like 2 negatively regulates the immune function of dendritic cells by suppressing autophagy via the TAK1/JNK pathway in septic mice.Cell Death Dis. 2021 Oct 30;12(11):1032. doi: 10.1038/s41419-021-04327-x. Cell Death Dis. 2021. PMID: 34718337 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kumar V, Sharma A. Innate immunity in sepsis pathogenesis and its modulation: new immunomodulatory targets revealed. J Chemother 2008; 20: 672–683. - PubMed
-
- Vega-Ramos J, Roquilly A, Asehnoune K, et al. Modulation of dendritic cell antigen presentation by pathogens, tissue damage and secondary inflammatory signals. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2014; 17: 64–70. - PubMed
-
- Steinman RM, Hawiger D, Nussenzweig MC. Tolerogenic dendritic cells. Annu Rev Immunol 2003; 21: 685–711. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

