Retrospective study on the benefit of adjuvant radiotherapy in men with intraductal carcinoma of prostate
- PMID: 31018850
- PMCID: PMC6482557
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-019-1267-3
Retrospective study on the benefit of adjuvant radiotherapy in men with intraductal carcinoma of prostate
Abstract
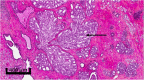
Background: Intraductal carcinoma of the prostate (IDC-P) is an independent biomarker of recurrence and survival with particular treatment response, yet no study has tested its response to radiotherapy. The aim of our project was to test the impact of adjuvant radiotherapy (ART) in patients with localized to locally advanced prostate cancer (PC) and IDC-P.
Materials and methods: We performed a retrospective study of men with pT2-T3 PC treated by radical prostatectomy (RP) with or without ART, from two centres (1993-2015). Exclusion criteria were the use of another type of treatment prior to biochemical recurrence (BCR), and detectable prostate- specific antigen (PSA) following RP or ART. Primary outcome was BCR (2 consecutive PSA ≥ 0.2 ng/ml). Patients were grouped by treatment (RPonly/RP + ART), IDC-P status, and presence of high-risk features (HRF: Grade Groups 4-5, positive margins, pT3 stage).
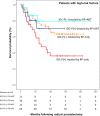
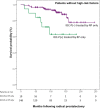
Results: We reviewed 293 RP specimens (median follow-up 99 months, 69 BCR). Forty-eight patients (16.4%) were treated by RP + ART. Multivariate Cox regression for BCR indicated that IDC-P had the strongest impact (hazard ratio [HR] = 2.39, 95% confidence interval [CI]:1.44-3.97), while ART reduced the risk of BCR (HR = 0.38, 95%CI: 0.17-0.85). Other HRF were all significant except for pT3b stage. IDC-P[+] patients who did not receive ART had the worst BCR-free survival (log-rank P = 0.023). Furthermore, IDC-P had the same impact on BCR-free survival as ≥1 HRF (log-rank P = 0.955).
Conclusion: Men with IDC-P who did not receive ART had the highest BCR rates, and IDC-P had the same impact as ≥1 HRF, which are often used as ART indications. Once validated, ART should be considered in patients with IDC-P.
Keywords: Adjuvant radiotherapy; Biochemical recurrence; Prostate cancer; Radical prostatectomy.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethics committee approval and consent to participate were obtained.
Consent for publication
All authors approved the manuscript for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


References
-
- Kato Masashi, Tsuzuki Toyonori, Kimura Kyosuke, Hirakawa Akihiro, Kinoshita Fumie, Sassa Naoto, Ishida Ryo, Fukatsu Akitoshi, Kimura Tohru, Funahashi Yasuhito, Matsukawa Yoshihisa, Hattori Ryohei, Gotoh Momokazu. The presence of intraductal carcinoma of the prostate in needle biopsy is a significant prognostic factor for prostate cancer patients with distant metastasis at initial presentation. Modern Pathology. 2016;29(2):166–173. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2015.146. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

