Targeting the NFAT:AP-1 transcriptional complex on DNA with a small-molecule inhibitor
- PMID: 31019078
- PMCID: PMC6525529
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1820604116
Targeting the NFAT:AP-1 transcriptional complex on DNA with a small-molecule inhibitor
Abstract
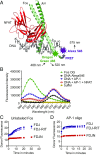
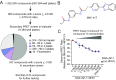
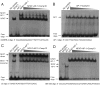
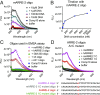
The transcription factor nuclear factor of activated T cells (NFAT) has a key role in both T cell activation and tolerance and has emerged as an important target of immune modulation. NFAT directs the effector arm of the immune response in the presence of activator protein-1 (AP-1), and T cell anergy/exhaustion in the absence of AP-1. Envisioning a strategy for selective modulation of the immune response, we designed a FRET-based high-throughput screen to identify compounds that disrupt the NFAT:AP-1:DNA complex. We screened ∼202,000 small organic compounds and identified 337 candidate inhibitors. We focus here on one compound, N-(3-acetamidophenyl)-2-[5-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)pyridin-2-yl]sulfanylacetamide (Compound 10), which disrupts the NFAT:AP-1 interaction at the composite antigen-receptor response element-2 site without affecting the binding of NFAT or AP-1 alone to DNA. Compound 10 binds to DNA in a sequence-selective manner and inhibits the transcription of the Il2 gene and several other cyclosporin A-sensitive cytokine genes important for the effector immune response. This study provides proof-of-concept that small molecules can inhibit the assembly of specific DNA-protein complexes, and opens a potential new approach to treat human diseases where known transcription factors are deregulated.
Keywords: FRET assay; Fos; Jun; NFAT; cyclosporin A.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: A.R. and P.G.H. are founders of CalciMedica, Inc., and members of its scientific advisory board.
Figures


References
-
- Rao A, Luo C, Hogan PG. Transcription factors of the NFAT family: Regulation and function. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:707–747. - PubMed
-
- Hogan PG, Chen L, Nardone J, Rao A. Transcriptional regulation by calcium, calcineurin, and NFAT. Genes Dev. 2003;17:2205–2232. - PubMed
-
- Macian F. NFAT proteins: Key regulators of T-cell development and function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2005;5:472–484. - PubMed
-
- Baksh S, DeCaprio JA, Burakoff SJ. Calcineurin regulation of the mammalian G0/G1 checkpoint element, cyclin dependent kinase 4. Oncogene. 2000;19:2820–2827. - PubMed
-
- Jauliac S, et al. The role of NFAT transcription factors in integrin-mediated carcinoma invasion. Nat Cell Biol. 2002;4:540–544. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

