Structural mechanism for Bruton's tyrosine kinase activation at the cell membrane
- PMID: 31019091
- PMCID: PMC6511029
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1819301116
Structural mechanism for Bruton's tyrosine kinase activation at the cell membrane
Abstract
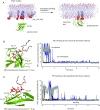
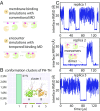
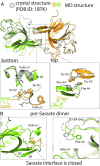
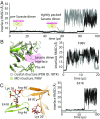
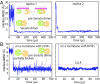
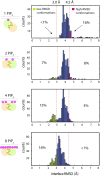
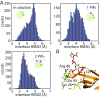
Bruton's tyrosine kinase (Btk) is critical for B cell proliferation and activation, and the development of Btk inhibitors is a vigorously pursued strategy for the treatment of various B cell malignancies. A detailed mechanistic understanding of Btk activation has, however, been lacking. Here, inspired by a previous suggestion that Btk activation might depend on dimerization of its lipid-binding PH-TH module on the cell membrane, we performed long-timescale molecular dynamics simulations of membrane-bound PH-TH modules and observed that they dimerized into a single predominant conformation. We found that the phospholipid PIP3 stabilized the dimer allosterically by binding at multiple sites, and that the effects of PH-TH mutations on dimer stability were consistent with their known effects on Btk activity. Taken together, our simulation results strongly suggest that PIP3-mediated dimerization of Btk at the cell membrane is a critical step in Btk activation.
Keywords: Bruton’s tyrosine kinase; PIP3; allosteric activation; dimerization; enhanced sampling.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
E41K mutation activates Bruton's tyrosine kinase by stabilizing an inositol hexakisphosphate-dependent invisible dimer.J Biol Chem. 2024 Aug;300(8):107535. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2024.107535. Epub 2024 Jul 4. J Biol Chem. 2024. PMID: 38971313 Free PMC article.
-
Switch-like activation of Bruton's tyrosine kinase by membrane-mediated dimerization.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 May 28;116(22):10798-10803. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1819309116. Epub 2019 May 10. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31076553 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional requirement for dimerization of the membrane-binding module for BTK signaling in lymphocyte cell lines.Sci Signal. 2025 Jan 14;18(869):eado1252. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.ado1252. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Sci Signal. 2025. PMID: 39808693 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Bruton's tyrosine kinase in B cells and malignancies.Mol Cancer. 2018 Feb 19;17(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0779-z. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29455639 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Development of Bruton's Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors for Rheumatoid Arthritis.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(42):5847-5859. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180316121951. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29546831 Review.
Cited by
-
Systematic simulation of the interactions of pleckstrin homology domains with membranes.Sci Adv. 2022 Jul 8;8(27):eabn6992. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn6992. Epub 2022 Jul 6. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35857458 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid-targeting pleckstrin homology domain turns its autoinhibitory face toward the TEC kinases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Oct 22;116(43):21539-21544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1907566116. Epub 2019 Oct 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31591208 Free PMC article.
-
PROTAC'ing oncoproteins: targeted protein degradation for cancer therapy.Mol Cancer. 2023 Mar 30;22(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01707-5. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36991452 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PROTACs to address the challenges facing small molecule inhibitors.Eur J Med Chem. 2021 Jan 15;210:112993. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112993. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Eur J Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 33189436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Orally bioavailable BTK PROTAC active against wild-type and C481 mutant BTKs in human lymphoma CDX mouse models.Blood Adv. 2023 Jan 10;7(1):92-105. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022008121. Blood Adv. 2023. PMID: 36269842 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindvall JM, et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase: Cell biology, sequence conservation, mutation spectrum, siRNA modifications, and expression profiling. Immunol Rev. 2005;203:200–215. - PubMed
-
- Dal Porto JM, et al. B cell antigen receptor signaling 101. Mol Immunol. 2004;41:599–613. - PubMed
-
- Jefferies CA, et al. Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is a Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-binding protein that participates in nuclear factor kappaB activation by Toll-like receptor 4. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:26258–26264. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

