XFEL structures of the human MT2 melatonin receptor reveal the basis of subtype selectivity
- PMID: 31019305
- PMCID: PMC6589158
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-019-1144-0
XFEL structures of the human MT2 melatonin receptor reveal the basis of subtype selectivity
Abstract
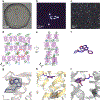
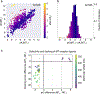
The human MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors1,2 are G-protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that help to regulate circadian rhythm and sleep patterns3. Drug development efforts have targeted both receptors for the treatment of insomnia, circadian rhythm and mood disorders, and cancer3, and MT2 has also been implicated in type 2 diabetes4,5. Here we report X-ray free electron laser (XFEL) structures of the human MT2 receptor in complex with the agonists 2-phenylmelatonin (2-PMT) and ramelteon6 at resolutions of 2.8 Å and 3.3 Å, respectively, along with two structures of function-related mutants: H2085.46A (superscripts represent the Ballesteros-Weinstein residue numbering nomenclature7) and N862.50D, obtained in complex with 2-PMT. Comparison of the structures of MT2 with a published structure8 of MT1 reveals that, despite conservation of the orthosteric ligand-binding site residues, there are notable conformational variations as well as differences in [3H]melatonin dissociation kinetics that provide insights into the selectivity between melatonin receptor subtypes. A membrane-buried lateral ligand entry channel is observed in both MT1 and MT2, but in addition the MT2 structures reveal a narrow opening towards the solvent in the extracellular part of the receptor. We provide functional and kinetic data that support a prominent role for intramembrane ligand entry in both receptors, and suggest that there might also be an extracellular entry path in MT2. Our findings contribute to a molecular understanding of melatonin receptor subtype selectivity and ligand access modes, which are essential for the design of highly selective melatonin tool compounds and therapeutic agents.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
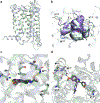

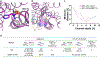

Similar articles
-
Structural basis of ligand recognition at the human MT1 melatonin receptor.Nature. 2019 May;569(7755):284-288. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1141-3. Epub 2019 Apr 24. Nature. 2019. PMID: 31019306 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of the ligand binding and signaling mechanism of melatonin receptors.Nat Commun. 2022 Jan 24;13(1):454. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28111-3. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35075127 Free PMC article.
-
Quantum mechanics insights into melatonin and analogs binding to melatonin MT1 and MT2 receptors.Sci Rep. 2024 May 13;14(1):10922. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59786-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38740789 Free PMC article.
-
Homology models of melatonin receptors: challenges and recent advances.Int J Mol Sci. 2013 Apr 12;14(4):8093-121. doi: 10.3390/ijms14048093. Int J Mol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23584026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MT1 and MT2 Melatonin Receptors: A Therapeutic Perspective.Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016;56:361-83. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010814-124742. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 26514204 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A host dTMP-bound structure of T4 phage dCMP hydroxymethylase mutant using an X-ray free electron laser.Sci Rep. 2019 Nov 8;9(1):16316. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-52825-y. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31705139 Free PMC article.
-
Serial femtosecond crystallography.Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2022 Aug 4;2:59. doi: 10.1038/s43586-022-00141-7. Nat Rev Methods Primers. 2022. PMID: 36643971 Free PMC article.
-
Virtual discovery of melatonin receptor ligands to modulate circadian rhythms.Nature. 2020 Mar;579(7800):609-614. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2027-0. Epub 2020 Feb 10. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32040955 Free PMC article.
-
Ligand binding at the protein-lipid interface: strategic considerations for drug design.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021 Sep;20(9):710-722. doi: 10.1038/s41573-021-00240-2. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021. PMID: 34257432 Review.
-
Melatonin-mediated cGAS-STING signal in senescent macrophages promote TNBC chemotherapy resistance and drive the SASP.J Biol Chem. 2025 May;301(5):108438. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2025.108438. Epub 2025 Mar 22. J Biol Chem. 2025. PMID: 40127867 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Karamitri A et al. Type 2 diabetes-associated variants of the MT2 melatonin receptor affect distinct modes of signaling. Sci Signal 11, eaan6622 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

