Radiological aspects in computed tomography as determinants in the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in immunocompetent infants
- PMID: 31019334
- PMCID: PMC6472858
- DOI: 10.1590/0100-3984.2018.0025
Radiological aspects in computed tomography as determinants in the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in immunocompetent infants
Abstract
Objective: To describe the chest computed tomography (CT) findings in immunocompetent children under 36 months of age with pulmonary tuberculosis.
Materials and methods: This was a descriptive case series conducted in the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, between January 2004 and July 2013, involving 20 young children who underwent CT after undergoing chest X-rays that did not provide a definitive diagnosis.
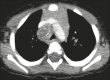
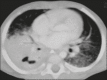
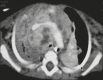
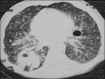
Results: All of the participants had lymph node enlargement and consolidations. In 15 cases (75%), the consolidations were accompanied by atelectasis. Pulmonary cavitation was seen in 10 cases (50%), and cavitation within consolidations was seen in 7 (35%). The areas of cavitation and parenchymal destruction were not seen on conventional chest X-rays.
Conclusion: The radiological presentation of pulmonary tuberculosis in young children differs from that described in older children and adults. CT is an effective method for the early diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in immunocompetent infants, allowing the rapid institution of specific treatment, which is crucial for halting disease progression, as well as for preventing local and systemic complications.
Objetivo: Descrever achados radiológicos na tomografia computadorizada (TC) de tórax de crianças imunocompetentes menores de 36 meses com tuberculose pulmonar.
Materiais e métodos: Esta série de casos foi desenvolvida na cidade do Rio de Janeiro, no período de janeiro de 2004 a julho de 2013, onde 20 pacientes foram submetidos a TC após a realização de radiografias de tórax que não definiram o diagnóstico.
Resultados: Todos os participantes tiveram linfonodomegalias e consolidações. Em 15 casos (75%) as consolidações tiveram atelectasia associada. Escavações pulmonares ocorreram em 10 casos (50%), havendo consolidações em 7 (35%). Áreas de escavação e destruição parenquimatosa em fase inicial não foram observadas nas radiografias simples.
Conclusão: A apresentação radiológica de tuberculose pulmonar em lactentes não foi a mesma descrita em crianças maiores e adultos. A TC é um método aplicável para o diagnóstico precoce de tuberculose pulmonar em lactentes imunocompetentes, permitindo a rápida instituição de tratamento específico, que é crucial para interromper a progressão da doença e prevenir suas complicações locais e sistêmicas.
Keywords: Children; Computed tomography; Tuberculosis, pulmonary.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Role of HRCT in the identification of atypical pulmonary mycobacteriosis.Radiol Med. 2002 Mar;103(3):158-70. Radiol Med. 2002. PMID: 11976613 English, Italian.
-
Pulmonary tuberculosis in infants: radiographic and CT findings.AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006 Oct;187(4):1024-33. doi: 10.2214/AJR.04.0751. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006. PMID: 16985152
-
Radiological Manifestations of Pulmonary Tuberculosis - A Comparative Study between Immunocompromised and Immunocompetent Patients.J Clin Diagn Res. 2017 Sep;11(9):TC06-TC09. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2017/28183.10535. Epub 2017 Sep 1. J Clin Diagn Res. 2017. PMID: 29207803 Free PMC article.
-
Chest X-ray and chest CT findings in patients diagnosed with pulmonary tuberculosis following solid organ transplantation: a systematic review.J Bras Pneumol. 2018 Apr;44(2):161-166. doi: 10.1590/s1806-37562017000000459. J Bras Pneumol. 2018. PMID: 29791554 Free PMC article.
-
[Should pulmonary computed tomography be performed in children with tuberculosis infection without apparent disease?].An Pediatr (Barc). 2007 Dec;67(6):585-93. An Pediatr (Barc). 2007. PMID: 18053526 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Identifying immunodeficiency status in children with pulmonary tuberculosis: using radiomics approach based on un-enhanced chest computed tomography.Transl Pediatr. 2023 Dec 26;12(12):2191-2202. doi: 10.21037/tp-23-309. Epub 2023 Dec 22. Transl Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 38197102 Free PMC article.
-
Pulmonary tuberculous pseudotumor in a pediatric patient--A diagnostic dilemma.J Postgrad Med. 2021 Jan-Mar;67(1):49-50. doi: 10.4103/jpgm.JPGM_209_20. J Postgrad Med. 2021. PMID: 33380590 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global tuberculosis report. Geneva: WHO; 2017. [2017 Dec 5]. Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/259366/1/9789241565516-eng.pdf?....
-
- Marais BJ, Gie RP, Hesseling AC, et al. A refined symptom-based approach to diagnose pulmonary tuberculosis in children. Pediatrics. 2006;118:e1350–e1359. - PubMed
-
- Secretaria de Estado de Saúde do Rio de Janeiro Tuberculose. Boletim tuberculose 2014. [2017 Dec 5]. Available from: http://www.riocomsaude.rj.gov.br/Publico/MostrarArquivo.aspx?C=wXJ%2BKou....
-
- Griffith-Richards SB, Goussard P, Andronikou S, et al. Cavitating pulmonary tuberculosis in children: correlating radiology with pathogenesis. Pediatr Radiol. 2007;37:798–804. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
