Inhibition of Oxidative Neurotoxicity and Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment by γ-Mangostin: In Vitro and In Vivo Evidence
- PMID: 31019651
- PMCID: PMC6451816
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/3640753
Inhibition of Oxidative Neurotoxicity and Scopolamine-Induced Memory Impairment by γ-Mangostin: In Vitro and In Vivo Evidence
Abstract
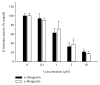
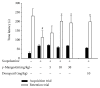
Among a series of xanthones identified from mangosteen, the fruit of Garcinia mangostana L. (Guttifereae), α- and γ-mangostins are known to be major constituents exhibiting diverse biological activities. However, the effects of γ-mangostin on oxidative neurotoxicity and impaired memory are yet to be elucidated. In the present study, the protective effect of γ-mangostin on oxidative stress-induced neuronal cell death and its underlying action mechanism(s) were investigated and compared to that of α-mangostin using primary cultured rat cortical cells. In addition, the effect of orally administered γ-mangostin on scopolamine-induced memory impairment was evaluated in mice. We found that γ-mangostin exhibited prominent protection against H2O2- or xanthine/xanthine oxidase-induced oxidative neuronal death and inhibited reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation triggered by these oxidative insults. In contrast, α-mangostin had no effects on the oxidative neuronal damage or associated ROS production. We also found that γ-mangostin, not α-mangostin, significantly inhibited H2O2-induced DNA fragmentation and activation of caspases 3 and 9, demonstrating its antiapoptotic action. In addition, only γ-mangostin was found to effectively inhibit lipid peroxidation and DPPH radical formation, while both mangostins inhibited β-secretase activity. Furthermore, we observed that the oral administration of γ-mangostin at dosages of 10 and 30 mg/kg markedly improved scopolamine-induced memory impairment in mice. Collectively, these results provide both in vitro and in vivo evidences for the neuroprotective and memory enhancing effects of γ-mangostin. Multiple mechanisms underlying this neuroprotective action were suggested in this study. Based on our findings, γ-mangostin could serve as a potentially preferable candidate over α-mangostin in combatting oxidative stress-associated neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer's disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mangosteen Pericarp and Its Bioactive Xanthones: Potential Therapeutic Value in Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, and Depression with Pharmacokinetic and Safety Profiles.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 27;21(17):6211. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176211. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32867357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antitumour and free radical scavenging effects of γ-mangostin isolated from Garcinia mangostana pericarps against hepatocellular carcinoma cell.J Pharm Pharmacol. 2013 Sep;65(9):1419-28. doi: 10.1111/jphp.12111. Epub 2013 Jul 15. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23927480
-
Protective Effect of γ-mangostin Isolated from the Peel of Garcinia mangostana against Glutamate-Induced Cytotoxicity in HT22 Hippocampal Neuronal Cells.Biomolecules. 2021 Jan 27;11(2):170. doi: 10.3390/biom11020170. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33514017 Free PMC article.
-
Natural Xanthones from Garcinia mangostana with Multifunctional Activities for the Therapy of Alzheimer's Disease.Neurochem Res. 2016 Jul;41(7):1806-17. doi: 10.1007/s11064-016-1896-y. Epub 2016 Apr 2. Neurochem Res. 2016. PMID: 27038926
-
α-Mangostin: A Xanthone Derivative in Mangosteen with Potent Anti-Cancer Properties.Biomolecules. 2024 Oct 30;14(11):1382. doi: 10.3390/biom14111382. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39595559 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Mechanistic Review on Protective Effects of Mangosteen and its Xanthones Against Hazardous Materials and Toxins.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024;22(12):1986-2015. doi: 10.2174/1570159X22666240212142655. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38486389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effects and Mechanisms of Xanthones in Alzheimer's Disease: A Systematic Review.Neurochem Res. 2023 Dec;48(12):3485-3511. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04005-8. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Neurochem Res. 2023. PMID: 37578655
-
Mangosteen Pericarp and Its Bioactive Xanthones: Potential Therapeutic Value in Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, and Depression with Pharmacokinetic and Safety Profiles.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 27;21(17):6211. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176211. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32867357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research progress of PPARγ regulation of cholesterol and inflammation in Alzheimer's disease.Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Mar;38(3):839-854. doi: 10.1007/s11011-022-01139-6. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Metab Brain Dis. 2023. PMID: 36723831 Review.
-
Mangostanaxanthone IV Ameliorates Streptozotocin-Induced Neuro-Inflammation, Amyloid Deposition, and Tau Hyperphosphorylation via Modulating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β Pathway.Biology (Basel). 2021 Dec 8;10(12):1298. doi: 10.3390/biology10121298. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34943213 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Halliwell B., Gutteridge J. M. C. Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine. Oxford: Clarendon Press; 1989.
-
- Manoharan S., Guillemin G. J., Abiramasundari R. S., Essa M. M., Akbar M., Akbar M. D. The role of reactive oxygen species in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and Huntington’s disease: a mini review. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity. 2016;2016:15. doi: 10.1155/2016/8590578.8590578 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

