Efficacy of 50 mg pregabalin for prevention of postoperative neuropathic pain after video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery and thoracotomy: a 3-month prospective randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 31019756
- PMCID: PMC6462706
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2019.02.77
Efficacy of 50 mg pregabalin for prevention of postoperative neuropathic pain after video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery and thoracotomy: a 3-month prospective randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: This study analyzed the preventive effect of 50 mg/day pregabalin on postoperative neuropathic pain, and any additional benefits related to sleep and respiratory function.
Methods: This prospective randomized controlled study included lung resection patients 20-89 years of age. Patients were randomly assigned to the treatment (pregabalin; initial dose, 50 mg/day) or control (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) group. Pregabalin patients received non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and pregabalin (25 mg, twice daily) from the second postoperative day. Pain scores, neuropathic pain, analgesic use, respiratory function, and insomnia scale scores for 3 months after surgery were evaluated.
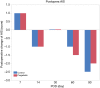
Results: This study included 46 patients who received pregabalin and 46 control patients. Pregabalin patients had significantly less postoperative neuropathic pain than control patients (19.6% vs. 41.3%; P=0.0404), and their duration of neuropathic pain was significantly shorter (30 vs. 90 days; P=0.024). The onset of postoperative neuropathic pain, insomnia scale scores, and respiratory function were similar between groups. No pregabalin-related adverse events were reported.
Conclusions: Pregabalin (50 mg/day) had a significant preventive effect on postoperative neuropathic pain after thoracic surgery, without side effects. Early postoperative administration of pregabalin would help prevent neuropathic pain and provide better pain control after thoracic surgery.
Keywords: Thoracic surgery; neuropathic pain; postoperative pain; pregabalin; video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: This study was presented at an international session of the 114th Annual Congress of the Japan Surgical Society by Takahiro Homma.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of oral pregabalin on postoperative sleep of patients after video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery: a randomized double-blind controlled trial.Minerva Anestesiol. 2024 Oct;90(10):872-881. doi: 10.23736/S0375-9393.24.18195-3. Minerva Anestesiol. 2024. PMID: 39381868 Clinical Trial.
-
Pregabalin reduces post-surgical pain after thoracotomy: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial.Surg Today. 2015 Nov;45(11):1411-6. doi: 10.1007/s00595-014-1088-9. Epub 2014 Nov 28. Surg Today. 2015. PMID: 25430812 Clinical Trial.
-
A prospective randomized study to analyze the efficacy of balanced pre-emptive analgesia in spine surgery.Spine J. 2019 Apr;19(4):569-577. doi: 10.1016/j.spinee.2018.10.010. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Spine J. 2019. PMID: 30359764 Clinical Trial.
-
Postoperative pain and quality of life after lobectomy via video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery or anterolateral thoracotomy for early stage lung cancer: a randomised controlled trial.Lancet Oncol. 2016 Jun;17(6):836-844. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)00173-X. Epub 2016 May 6. Lancet Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27160473 Clinical Trial.
-
Does video-assisted thoracic surgery provide a safe alternative to conventional techniques in patients with limited pulmonary function who are otherwise suitable for lung resection?Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013 Jul;17(1):159-62. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivt097. Epub 2013 Mar 26. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2013. PMID: 23532353 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PROSPECT guidelines for video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery: a systematic review and procedure-specific postoperative pain management recommendations.Anaesthesia. 2022 Mar;77(3):311-325. doi: 10.1111/anae.15609. Epub 2021 Nov 5. Anaesthesia. 2022. PMID: 34739134 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of add-on mirogabalin to conventional therapy for the treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain after thoracic surgery: the multicenter, randomized, open-label ADMIT-NeP study.BMC Cancer. 2024 Jan 15;24(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11708-2. BMC Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38225552 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The efficacy of pregabalin for pain control after thoracic surgery: a meta-analysis.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024 Jan 3;19(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13019-023-02449-1. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2024. PMID: 38172988 Free PMC article.
-
Preoperative umeclidinium/vilanterol or tiotropium improves postoperative FEV1 in lung cancer patients with comorbid untreated chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Apr 28;15(4):1584-1594. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-1704. Epub 2023 Mar 20. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 37197513 Free PMC article.
-
Intrathoracic oxygen detects alveolar air leak following video-assisted thoracoscopic lung resection.Sci Rep. 2025 Aug 30;15(1):31952. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-16882-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40883373 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
