Minimally Invasive Quadricepsplasty
- PMID: 31019888
- PMCID: PMC6472174
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eats.2018.11.005
Minimally Invasive Quadricepsplasty
Abstract
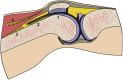
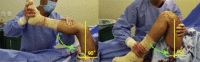
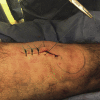
A modification of range of motion of the knee can significantly change a patient's quality of life. In general, range of motion of 0° to 125° is adequate for most activities of daily life. The rate of knee arthrofibrosis after ligament reconstruction is reported to be between 0% and 4%; after tibial fracture due to high-energy trauma, the rate is about 7%, with an undetermined incidence after limb lengthening. The purpose of this study was to describe a modification of the operative technique of Judet. We describe minimally invasive quadricepsplasty in 4 steps, aiming to obtain an end result with an arc of movement of at least 120° to 130°. We believe that our technique is a good option for the treatment of the stiff knee, having low morbidity and being an easy method to perform.
Figures
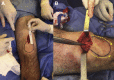
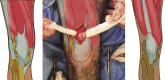
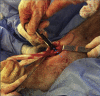
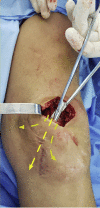
Similar articles
-
Minimally Invasive Quadricepsplasty Using the Adolphson-Cerqueira Technique: A Retrospective Study after 1-Year of Follow-up.Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2024 May-Aug;19(2):87-93. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10080-1615. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2024. PMID: 39359364 Free PMC article.
-
Thompson Versus Judet Techniques for Quadricepsplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Outcomes and Complications.JB JS Open Access. 2024 Jul 30;9(3):e24.00040. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.OA.24.00040. eCollection 2024 Jul-Sep. JB JS Open Access. 2024. PMID: 39081670 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modified judet quadricepsplasty and Ilizarov frame application for stiff knee after femur fractures.J Orthop Trauma. 2010 Nov;24(11):709-15. doi: 10.1097/BOT.0b013e3181c80bb9. J Orthop Trauma. 2010. PMID: 20881636
-
Prognostic Factors Affecting the Results of Modified Thompson Quadricepsplasty for the Treatment of Extension Contracture of the Knee.Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2017 Mar;5(2):109-113. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 2017. PMID: 28497101 Free PMC article.
-
Old but gold: Is the Judet procedure still a viable option for posttraumatic knee stiffness in 2024? A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis.J Exp Orthop. 2024 Nov 7;11(4):e70079. doi: 10.1002/jeo2.70079. eCollection 2024 Oct. J Exp Orthop. 2024. PMID: 39512905 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Quadriceps strength and knee joint function in patients with severe knee extension contracture following arthroscopic-assisted mini-incision quadricepsplasty.Int Orthop. 2021 Nov;45(11):2869-2876. doi: 10.1007/s00264-021-04971-0. Epub 2021 Feb 11. Int Orthop. 2021. PMID: 33570669
-
[Effect of three-dimensional printing-assisted minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis on anti-malrotation for different types of tibial fractures].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Dec 15;33(12):1510-1515. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201903109. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31823549 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Minimally Invasive Quadricepsplasty Using the Adolphson-Cerqueira Technique: A Retrospective Study after 1-Year of Follow-up.Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2024 May-Aug;19(2):87-93. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10080-1615. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Strategies Trauma Limb Reconstr. 2024. PMID: 39359364 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Magit D., Wolff A., Sutton K., Medvecky M.J. Arthrofibrosis of the knee. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2007;15:682–694. - PubMed
-
- Shelbourne K.D., Nitz P. Accelerated rehabilitation after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Sports Med. 1990;18:292–299. - PubMed
-
- Egel K.A., Tejwani N.C., Capla E.L., Wolinsky P.L., Koval K.J. Staged management of high-energy proximal tibial fractures (OTA types 41): The results of a prospective, standardized protocol. J Orthop Trauma. 2005;19:448–455. - PubMed
-
- Thompson T. Quadricepsplasty to improve knee function. J Bone Joint Surg. 1944;26:366–379.
-
- Judet R. Mobilization of the stiff knee. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1959;41:856–857.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

