Is Stiff Person Syndrome Benefited by Physical Therapy Intervention? Summary of Case Reports
- PMID: 31019968
- PMCID: PMC6451805
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/5613680
Is Stiff Person Syndrome Benefited by Physical Therapy Intervention? Summary of Case Reports
Abstract
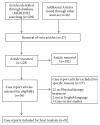
It is interesting to be aware that there is no Randomized Clinical Trials (RCT) research article except a few case-study reports which have been reported about the physical therapy (PT) intervention for stiff person syndrome (SPS). This study was designed to determine the benefits of PT in cases with SPS through analysis of case reports, thereby to raise awareness among physical therapist about the most beneficial PT interventions for SPS. We executed acomputer-based search with a diagnosis of SPS who underwent PT and articles published only in English. We selected case-study reports because of nonavailability of RCT articles to review the complaints, deformities, contractures, precipitating factors, interventions, outcomes, results, disability, and benefits of PT management among SPS. We concluded that PT training is substantiated to be a necessary and beneficial intervention in rehabilitation of patients with SPS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The effect of clinical pilates-based physiotherapy program for a Stiff Person Syndrome patient: a case report.Acta Neurol Belg. 2021 Feb;121(1):79-85. doi: 10.1007/s13760-020-01502-3. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Acta Neurol Belg. 2021. PMID: 32997327
-
Physical therapy during in-patient rehabilitation for a patient with Stiff-Person Syndrome.J Neurol Phys Ther. 2006 Mar;30(1):28-38. doi: 10.1097/01.npt.0000282147.18446.b8. J Neurol Phys Ther. 2006. PMID: 16630369
-
[Stiff person syndrome (Moersch-Woltman)].Lijec Vjesn. 2010 Mar-Apr;132(3-4):110-4. Lijec Vjesn. 2010. PMID: 20540439 Review. Croatian.
-
Stiff person syndrome.Front Neurol Neurosci. 2009;26:147-165. doi: 10.1159/000212375. Epub 2009 Apr 6. Front Neurol Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19349711 Review.
-
Stiff person syndrome.Pract Neurol. 2011 Oct;11(5):272-82. doi: 10.1136/practneurol-2011-000071. Pract Neurol. 2011. PMID: 21921002 Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of clinical pilates-based physiotherapy program for a Stiff Person Syndrome patient: a case report.Acta Neurol Belg. 2021 Feb;121(1):79-85. doi: 10.1007/s13760-020-01502-3. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Acta Neurol Belg. 2021. PMID: 32997327
-
Efficacy and safety of therapeutic plasma exchange in stiff person syndrome.Open Med (Wars). 2021 Mar 30;16(1):526-531. doi: 10.1515/med-2021-0220. eCollection 2021. Open Med (Wars). 2021. PMID: 33821220 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pediatric stiff-person syndrome and related disorders: A systematic review.Neurol Sci. 2025 Aug 19. doi: 10.1007/s10072-025-08397-z. Online ahead of print. Neurol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40826302 Review.
-
Improving Ambulation and Minimizing Disability with Therapeutic Plasma Exchange in a Stiff-person Syndrome Patient with Recurrent Falls.Cureus. 2019 Nov 20;11(11):e6209. doi: 10.7759/cureus.6209. Cureus. 2019. PMID: 31890410 Free PMC article.
-
Immunological, Physical, and Psychological Interventions in Young-Onset Stiff-Person Syndrome.J Clin Neurol. 2022 Jul;18(4):487-488. doi: 10.3988/jcn.2022.18.4.487. J Clin Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35796276 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Stiff Person Syndrome. Rare Disease Database. 2017. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/stiff-person-syndrome/
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources