Fleckenstein's hypothesis revisited: excessive myocardial calcification after prolonged high dose catecholamine treatment: a case report
- PMID: 31020202
- PMCID: PMC6426089
- DOI: 10.1093/ehjcr/yty126
Fleckenstein's hypothesis revisited: excessive myocardial calcification after prolonged high dose catecholamine treatment: a case report
Abstract
Background: Myocardial calcification after prolonged highly dosed catecholamine treatment has been described experimentally. Here, we demonstrate myocardial calcifications by high-dose catecholamine treatment leading to chronic heart failure in patients.
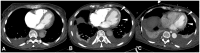
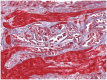
Case summary: A 62-year-old Caucasian woman presented with central pulmonary embolism, developing acute heart failure, and cardiogenic shock. Twenty-six days of high-dose norepinephrine treatment had to be administered to maintain circulation. After 74 days of intensive care treatment, the patient fortunately recovered but was readmitted to emergency ward because of dyspnoea and congestion. Computed tomography pulmonary angiography ruled out recurrence of pulmonary embolism, but depicted massive intramural cardiac calcifications, which were not present before treatment. Coronary angiography showed normal coronary arteries, and myocardial biopsy excluded infectious myocarditis. There was no evidence for sarcoidosis, thyroid disease, tuberculosis, or hyperparathyroidism. Oral heart failure treatment was initiated and at the 7 week follow-up the patient remained symptomatic with New York Heart Association functional Class III, while right and left ventricular function had recovered.
Discussion: Prolonged activation of the heart by catecholamines leading to myocardial calcifications has first been examined experimentally by Fleckenstein et al. Herein, we are able to show, that this can occur in clinical situations. Careful dosing of catecholamines and early use of non-catecholamine-based haemodynamic support is recommended to avoid consecutive impairment of heart function and heart failure.
Keywords: Case report; Catecholamines; Congestive heart failure; Myocardial calcification; Myocardium.
Figures

References
-
- Fleckenstein A, Kanke J, Döring HJ, Leder O.. Key role of Ca in the production of noncoronarogenic myocardial necroses. Recent Adv Stud Cardiac Struct Metab 1975;6:21–32. - PubMed
-
- Böhm M, Brückner R, Schäfer H, Schmitz W, Scholz H.. Inhibition of the effects of adenosine on force of contraction and the slow calcium inward current by pertussis toxin is associated with myocardial lesions. Cardiovasc Res 1988;22:87–94. - PubMed
-
- Lyon AR, Rees PS, Prasad S, Poole-Wilson PA, Harding SE.. Stress (Takotsubo) cardiomyopathy—a novel pathophysiological hypothesis to explain catecholamine-induced acute myocardial stunning. Nat Rev Cardiol 2008;5:22–29. - PubMed
-
- Freeman J, Dodd JD, Ridge CA, O'Neill A, McCreery C, Quinn M.. “Porcelain heart” cardiomyopathy secondary to hyperparathyroidism: radiographic, echocardiographic, and cardiac CT appearances. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 2010;4:402–404. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
